
The Effect of On-Street Parking in the Kelapa Lima Beach Area on
Traffic Performance on Timor Raya Street Kupang City
Amy Wadu, Mateus R. Sodanango and Obed Nenobais
Civil Engineering Department, Politeknik Negeri Kupang, Adi Sucipto Street, Kupang, Indonesia
Keywords: Capacity, Kupang, PKJI2014, Traffic, Urban Road.
Abstract: The increase in population and density of vehicles in urban areas results in a decrease in road performance
which ultimately causes traffic congestion problems. An increase in the vehicle population along with a
shortage of urban road space caused by roadside activities. One of them is the problem of parking on the road
because there is no adequate parking space will result in a decrease in road capacity which has an impact on
decreasing traffic performance on the road. The Kelapa Lima Beach area which is located on Timor Raya
street is a new refreshing place for residents of Kupang City but does not have adequate parking facilities.
Visitors park their vehicles on the road, causing the road capacity to decrease. This if allowed to continue will
have a bad impact on all social aspects. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of on-street
parking on traffic performance on the Timor Raya segment. The analysis method uses the Indonesian Road
Capacity Guidelines (PKJI 2014). The results show that on-street parking in the Kelapa Lima beach area has
an effect of 79.84 percent on traffic performance on the Timor Raya Street.
1 INTRODUCTION
On rapid economic development and motorization,
the number of motorized vehicles owned by residents
in various cities has increased significantly. At the
same time, the availability of transport infrastructure
lags behind, causing an imbalance between transport
demand and supply. This problem is especially
noticeable in the vehicle parking system. In some
areas of downtown Kupang, traffic is often heavy and
parking spaces are very limited. Thus, most users rely
on on-street parking facilities (Wadu, Tuati, and
Sodanango 2020) (Wadu, Loden, and Bria 2019)
(Wadu 2020).
On-street parking is often found in urban street
environments, because it is easy and does not require
a special parking space. Unfortunately, on-street
parking spaces are also associated with reduced road
capacity, which can result in reduced traffic
performance and an impact on accidents when
compared to roads of the same category without on-
street parking (Edquist, Rudin-Brown, and Lenné
2012).
One of the new congestion points in Kupang City
is the Kelapa Lima Beach area. The Kelapa Lima
Beach area development project which will be used
as the location of a culinary center in Kupang City,
East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia Although the project
has not been completed and has not been inaugurated,
the Culinary Center area is already crowded with
residents of Kupang on weekends. Many residents of
Kupang City came to meet the location which is
located in front of the Aston Kupang Hotel, on timor
raya street. The unavailability of parking facilities in
the area causes visitors to use the road as a parking
area which then affects the capacity of the highway
and causes a decrease in speed and traffic
performance on Timor Raya street in the area. Thus,
with increasing parking frequency and with
increasing traffic volume, this has the potential to
become a cause of congestion (Gore et al. 2021).
Several studies have been conducted on the
existence of parking on the road band which affects
the traffic performance parameters. On research (Et.
al. 2021) using the 1997 Indonesian Road Capacity
Manual (MKJI) and linear regression as the basis for
calculating all data, the R value is more than 0.8
which means that on-street parking has a strong
influence on vehicle travel time to pass H. Agus
Salim street. On research (Honma and Meguro 2020)
explains that in the downtown area of Yangon city,
Myanmar, which often experiences heavy traffic, also
shows that one of the reasons is the rampant illegal
1030
Wadu, A., Sodanango, M. and Nenobais, O.
The Effect of On-Street Parking in the Kelapa Lima Beach Area on Traffic Performance on Timor Raya Street Kupang City.
DOI: 10.5220/0012048200003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 1030-1034
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

parking of cars on the streets. On (Abu 2019)
explains the average total segment delay of the total
duration along the road segment due to roadside
parking on the 3 road segments studied in Addis
Ababa, Ethiopia was 7.29, 12.01 and 25.95 seconds
per vehicle. On research (Nahry et al. 2019) on
Jatinegara Barat street, Jakarta there is a fairly strong
relationship between parking and vehicle delays
moving to the parking location, and traffic volume
also affects this relationship.
Seeing that the traffic conditions in the Kelapa
Lima Beach area are increasingly congested, the
purpose of this study is to find out how much
influence parking vehicles have on the road to traffic
performance has a high urgency.
2 REVIEW OF LITERATURE
2.1 Side Friction
Side friction are defined as activities that occur on the
side of the road starting from lowering transportation
activities that affect normal traffic lanes that pass
through the road section (Forde and Daniel 2017).
Roadside activities affect traffic flow operations and
can cause delays, there are several references that try
to measure the effect directly especially for
developing countries where the effect tends to be high
(Ryus et al. 2011).
When side friction are at their worst, road capacity
is also reduced, resulting in traffic congestion
problems. On research (Pal and Roy 2019) shows the
road segment capacity decreased to 800 vehicles/hour
from 1,950 vehicles/hour when the side friction rate
increased from 50 incidents to 130 incidents. On
research (Saw et al. 2019) capacity in the city of
Warangal, India is estimated at 2909 vehicles/hour
for road conditions with side friction. And the
capacity in the absence of side resistance is 3173
vehicles/hour. There is an approximately 9%
reduction in capacity due to side drag. On-street
parking reduces road capacity (Chen et al. 2017). In
general, side friction can be buses stopping at stops,
pedestrians walking along the side of the train track
and crossing randomly, parking on the street, exits
and entries from the approach road, slow moving
vehicles (P. Li and He 2016).
2.2 On Street Parking
On Street Parking is located on the side of the road
with limited number of parking spaces, therefore it is
suitable for short term temporary parking users and
should have a higher parking turnover rate to provide
services to more users (J. Li, Wu, and Feng 2021).
There are several indicators that will be used to
correlate the effect between parking and traffic
performance, including parking volume and parking
accumulation (Wadu, Sulistio, and Wicaksono 2017).
Accumulation = Q
−Q
+Q
Where Q
in
is the number of vehicles entering every
hour, Q
out
is the number of vehicles exiting every
hour, and Q
s
is the number of vehicles parked on the
road before the observation.
Volume = Q
+Q
Where Q
in
is the number of vehicles entering every
hour and Q
s
is the number of vehicles that have been
parked on the road before the observation. side
2.3 Urban Road Performance
Urban road performance which is commonly called
Level of Service, LOS is a qualitative measure used
to indicate traffic conditions in terms of speed, travel
time, freedom to maneuver, comfort, convenience,
traffic disturbance, safety etc. The more the ratio, the
greater the congestion. v/c value of 1.0 indicates
heavy traffic. LOS suitable for various scenarios are
presented to deal with existing traffic problems
(Gajjar and Mohandas 2016).
On (Yany, Farida, and Walujodjati 2016) e
xplains traffic characteristics in terms of the V/C
Ratio and the average travel speed of traffic due to
parking on the road have a significant impact. When
the parking volume is high, the V/C Ratio is high and
the average travel time is low, causing congestion.
While on research (Yany, Farida, and Walujodjati
2016) t he existing condition on Ir.H Juanda street
with on-street parking apparently affects the
performance of Ir.H. Juanda street. The capacity of
roads without parking is 2,854 pcu/hour, while the
capacity with parking is 1,215 pcu/hour. For V/C
Ratio of 0.22. Average speed 33 km / h. The level of
service for peak hours on Ir.H. Juanda street is C.
Based on the Indonesian Road Capacity
Guidelines (PKJI 2014) traffic performance on urban
roads can be determined through a comparison
between the maximum hourly traffic flow and road
capacity. (PKJI 2014).
The Effect of On-Street Parking in the Kelapa Lima Beach Area on Traffic Performance on Timor Raya Street Kupang City
1031
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research stages start from literature study, data
collection, data analysis, to the results in the form of
conclusions and recommendations for handling. It
was started with a literature study which then
identified problems that caused traffic jams on the
Timor Raya road, especially in the Kelapa Lima
Beach area of Kupang City. This stage is carried out
to find out the real root problems that occur in the
study area. At this stage, the concentration points of
the study area and the scope of the problems to be
discussed are also carried out. The analysis stage is a
follow-up after data processing is completed. The
purpose of this stage is to understand and analyze the
processing results in depth. The analysis is carried out
by taking into account the traffic performance on the
section starting from the side friction and v/c ratio and
then proceeding with the parking volume to find out
how the effect of parking on traffic performance.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Traffic Flow
Observation of traffic flow is carried out for one week
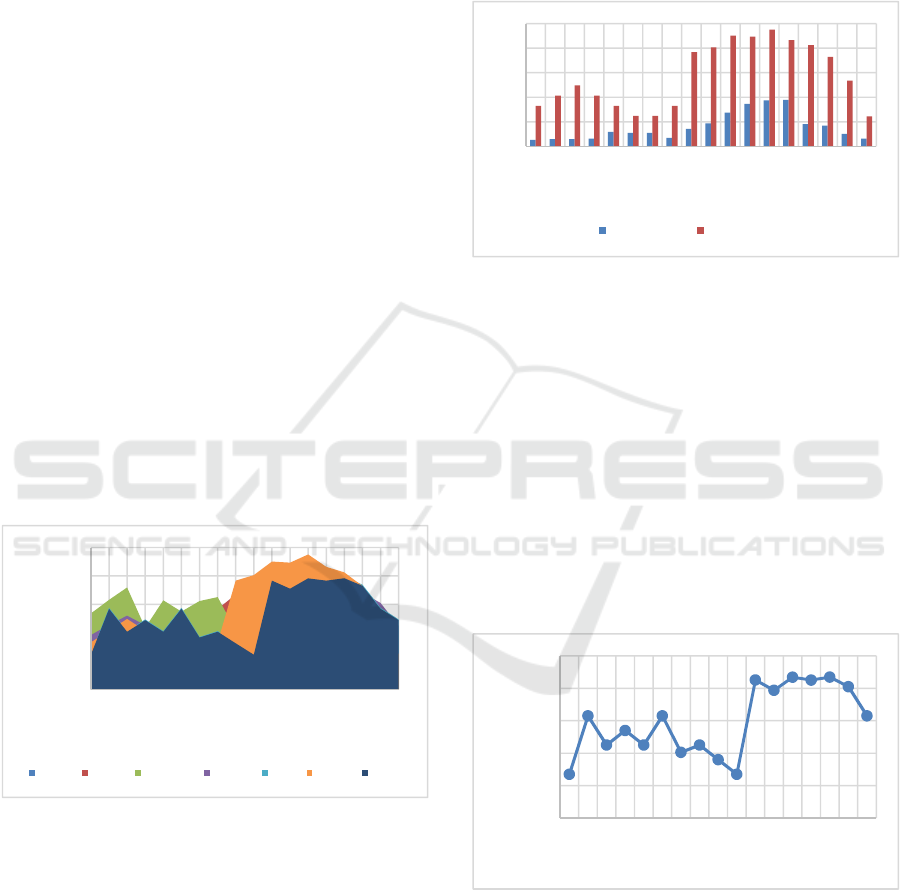
starting from 07.00 to 24.00 as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Traffic flow during one week observation.
Based on Figure 1, the peak traffic flow occurs on
Saturday at 19.00 with a value of 2378 cur/hour. This
condition occurs because Saturday is the weekend,
which generally Kupang City residents relax and
enjoy time with family. Meanwhile, the lowest traffic
flow occurred on Monday at 24.00 with a value of 420
cur/hour. This happens because Monday is a working
day where there are not many Kupang residents who
do tourism or relax.
4.2 Side Friction
As traffic conditions peak on Saturdays, it is
important to analyze roadside activity on Saturdays.
This side activity is a side friction for traffic flow on
the Timor Raya road.
Figure 2: Side friction on Saturday.
Based on Figure 2, the highest side resistance is at
20.00 with 945 incident frequencies. Meanwhile, at
19.00 which is the peak hour of traffic flow, the side
obstacle is at 934 the frequency of occurrence. This
shows that with this high traffic flow, there are also
high side friction, which means that the increase in
traffic flow also increases the activities of residents
on Kelapa Lima Beach.
4.3 Parking Accumulation
Road parking in the coconut five beach tourist area is
recorded on Saturday and is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Parking accumulation on Saturday.
Based on Figure 3, parking accumulation starts to
increase from 16.00 to 17.00 and starts constant at
17.00 to 22.00 with the highest accumulative
occurring at 21.00 with a value of 869 vehicles. This
also shows that high side friction and high traffic flow
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
7 8 9 101112131415161718192021222324
Traffic Flow (pcu)
Hours
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
Hours
Side Friction Traffic Flow
0
200
400
600
800
1000
7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
Parking Accumulation (pcu)
Hours
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1032
have a relationship with increasing accumulative
parking in the Kelapa Lima beach area.
4.4 Relationship Between Degree of
Saturation and Side Friction
Frequency
Higher side friction will affect the existing road
capacity. With the degree of saturation as a parameter
measuring how much capacity the road can meet the
traffic needs on the Timor Raya road, a model of the
relationship between side resistance and the degree of
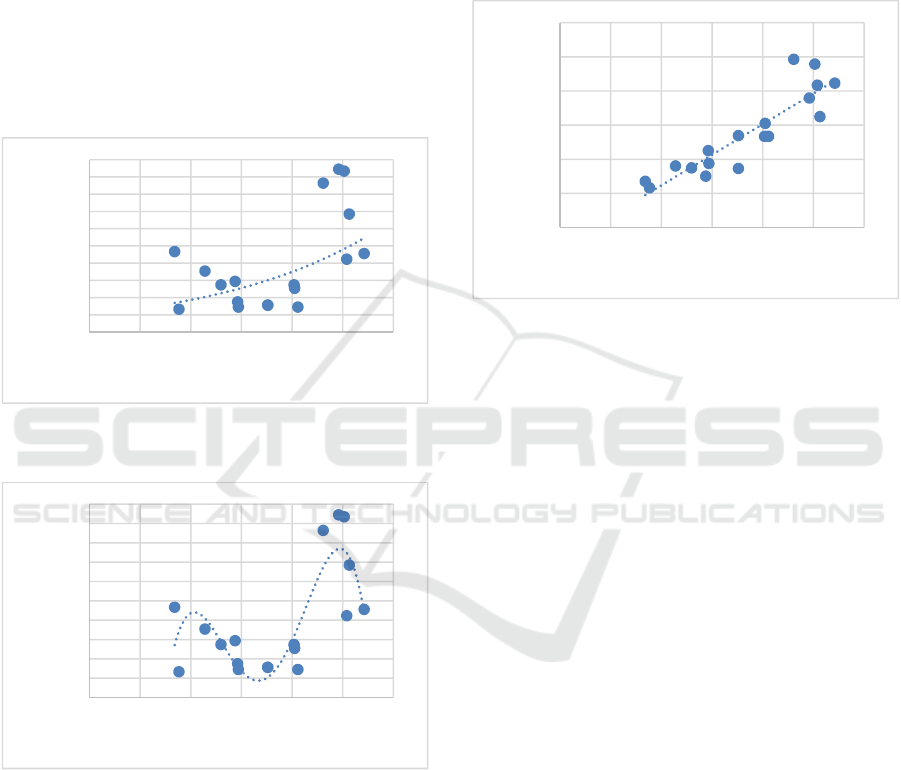
saturation is made in Figures 4 and 5.
Figure 4: Relationship between degree of saturation and
side friction frequency using exponential function.
Figure 5: Relationship between degree of saturation and
side friction frequency using polynomial of degree 4.
Figure 4 shows the relationship between the degree of
saturation and side resistance with the equation
y=100.02e1.5656x with R² = 0.3904 while in Figure
5 using the polynomial of degree 4 we get the
equation y = -73749x4 + 203436x3 - 198199x2 +
80436x – 11158 with R² = 0.7249 which is better than
the exponential function.
4.5 Relationship Between Degree of
Saturation and Parking
Accumulation
The relationship between the degree of saturation (x)
and parking accumulation (y) that occurs at the
Kelapa Lima beach is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 6: Relationship between degree of saturation and
parking accumulation.
Based on Figure 5, the more parking on the road body
will increase the degree of saturation of the road,
which means that the higher the degree of saturation,
the worse the road performance with the equation of
the relationship between y = 895.99x - 110.8 with R²
= 0.7984. This condition also explains that 79.84
percent of the degree of saturation can be affected by
on-street parking. The rest, as much as 0.16 or 20.16
percent are influenced by unknown variables.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the discussion of the effect of on-street
parking in the Kelapa Lima beach area, it has an effect
of 79.84 percent on traffic performance on the Timor
Raya road. So that in the future the government must
prepare parking facilities so that this will no longer
continue, let alone cause bigger problems.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks to Politeknik Negeri Kupang for providing
financial and moral assistance during the researchers
conducting this research.
y = 100,02e
1,5656x
R² = 0,3076
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
0,00 0,20 0,40 0,60 0,80 1,00 1,20
Side Friction Frequency
Degree of Saturation
y = -73749x
4
+ 203436x
3
- 198199x
2
+ 80436x -
11158
R² = 0,7249
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
0,00 0,20 0,40 0,60 0,80 1,00 1,20
Side Friction Frequency
Degree of Saturation
y = 895,99x - 110,8
R² = 0,7984
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0,00 0,20 0,40 0,60 0,80 1,00 1,20
Parking Accumulation (pcu)
Degree of Saturation
The Effect of On-Street Parking in the Kelapa Lima Beach Area on Traffic Performance on Timor Raya Street Kupang City
1033

REFERENCES
Abu, Taye. (2019). “Evaluation of Parking Problems for
Transportation System in Addis Ababa-A Case Study.”
International Journal for Research in Applied Science
and Engineering Technology 7(9).
Chen, Jingxu et al. (2017). “Simulating the Impacts of On-
Street Vehicle Parking on Traffic Operations on Urban
Streets Using Cellular Automation.” Physica A:
Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 468.
Edquist, Jessica, Christina M. Rudin-Brown, and Michael
G. Lenné. (2012). “The Effects of On-Street Parking
and Road Environment Visual Complexity on Travel
Speed and Reaction Time.” Accident Analysis and
Prevention 45: 759–65.
Et. al., Stella Belinda Kartika Putri. (2021). “Analysis of the
Relationship Between Travel Time and on Street
Parking.” Turkish Journal of Computer and
Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT) 12(3).
Forde, Albert, and Janice Daniel. (2017). “Performance
Evaluation of the HCM 2010 Platoon Dispersion Model
under Midblock Pedestrian and Truck Traffic Friction
Conditions.” Journal of Traffic and Transportation
Engineering (English Edition) 4(6).
Gajjar, Rajesh, and Divya Mohandas. (2016). “Critical
Assessment of Road Capacities on Urban Roads - A
Mumbai Case-Study.” In Transportation Research
Procedia,.
Gore, Ninad et al. (2021). “Effect of On-Street Parking on
Pedestrian Flow Characteristics and Level of Service -
an Indian Viewpoint.” Case Studies on Transport
Policy 9(3).
Honma, Yudai, and Kimiro Meguro. (2020). “Traffic
Impacts of On-Street Parking Cars on Secondary North-
South Streets in Downtown Yangon.” Journal of
Disaster Research 15(4).
Li, Jun, Sifan Wu, and Xiaoman Feng. (2021).
“Optimization of On-Street Parking Charges Based on
Price Elasticity of the Expected Perceived Parking
Cost.” Sustainability (Switzerland) 13(10).
Li, Peiqing, and Jie He. (2016). “Geometric Design Safety
Estimation Based on Tire-Road Side Friction.”
Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies 63.
Nahry, Heddy R. Agah, Antho Thohirin, and Nor Hayati
Abdul Hamid. (2019). “Modeling the Relationship
between On-Street Parking Characteristics and through
Traffic Delay.” In Proceedings of the Pakistan
Academy of Sciences: Part A,.
Pal, Sudipta, and Sudip Kr Roy. (2019). “Impact of Side
Friction on Performance of Rural Highways in India.”
Journal of Infrastructure Systems 25(2).
PKJI. 2014. “Pedoman Kapasitas Jalan Indonesia.”
Panduan Kapasitas Jalan Indonesia.
Ryus, Paul et al. (2011). “Highway Capacity Manual 2010.”
TR News (273).
Saw, Krishna, Aathira K. Das, Bhimaji K. Katti, and
Gaurang J. Joshi. (2019). “Travel Time Estimation
Modelling under Heterogeneous Traffic: A Case Study
of Urban Traffic Corridor in Surat, India.” Periodica
Polytechnica Transportation Engineering 47(4).
Wadu, Amy. (2020). “Analysis Of Road Capacity And
Traffic Performance On Jendral Soeharto Street
Kupang.” Journal Innovation of Civil Engineering
(JICE) 1(1).
Wadu, Amy, Onisius Loden, and Theresia Bria. (2019).
“Analysis of Capacity and Level of Service (LoS) of
Piet A. Tallo Street Kupang, Indonesia.”
Wadu, Amy, Harnen Sulistio, and Achmad Wicaksono.
(2017). “Kajian Kapasitas, Kebutuhan, Dan Efektivitas
Pakir Di Bandar Udara El Tari Kupang.” Rekayasa Sipil
11(1).
Yany, R. M., Farida, I., & Walujodjati, E. (2016). Pengaruh
Parkir Pada Badan Jalan Terhadap Kinerja Ruas Jalan
(Studi Kasus: Ruas Jalan Ciledug Kota Garut). Jurnal
Konstruksi, 14(1).
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1034
