
The Effects of Internet-Using on Farmer Employment Choice
and Income Differentiation:
An Empirical Study Based on the CGSS2017
Jie Liu
a
and Ti Wang
*b
School of Government, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, Peoples Republic China
Keywords: Internet-Using, Income Differentiation, Employment Choice, Multiple Regression Analysis, Farmer.
Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to study the impact of Internet-using on farmers income differentiation. Based
on the data of Chinese General Social Survey in 2017, this study uses Ordinary Least Square multiple
regression and Stata16 software to analyze model and data. By comparing the income levels of farmers who
use the Internet and those who do not use the Internet, this paper indicates that Internet-using affects income
differentiation by influencing farmers employment choices. The Internet-using can help farmers choose
more suitable jobs by information and communication technologies so that increasing their income. In
addition, in the further segmentation of non-agricultural employment, this paper studies the impact of the
Internet, and finds that Internet using has a positive impact on entrepreneurial employment, but a negative
impact on migrant employment. The empirical results show that Internet using is helpful to promote the
income differentiation of farmers.
1 INTRODUCTION
①
It is an important task in the new era to improve
farmers lives, mobilize their enthusiasm for
production and achieve common prosperity. With
the continuous improvement of rural Internet
infrastructure construction, Internet technology has
become an important carrier of farmers' production
and life. Farmers can not only find job opportunities
and conduct interviews on the Internet, but also
engage in agricultural e-commerce. According to the
50th Statistical Report on the Development of
Internet in China, as of June 2022, the number of
Internet users in China is 1051 million, and the
Internet penetration rate is 74.4%, including 293
million in rural areas, and the Internet penetration
rate is 58.8%.
1
The continuous expansion of the
Internet industry derived from the Internet has
significantly increased the income of some residents
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9317-009X.
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6993-3528.
1
Data source: The China Internet Information Center. The
50th Statistical Report on the Development of the Internet
in China, http: / / www.cnnic.net.cn/n4/2022/0914/c88-
10226.html.
living in rural areas, but at the same time, it has also
exacerbated the income gap between different
farmers. By using Internet, some farmers obtain the
information about employment, agricultural product
marketing, land circulation and find suitable jobs,
realizing the effective allocation of rural resources.
However, the others can't effectively use the Internet
to increase their income, which are limited by
Internet access conditions, their own age, education
and other factors. Based on this, this study uses OLS
multiple regression and Stata16 software to explore
whether Internet using aggravates the income
differentiation of farmers and how Internet use leads
to income differentiation of farmers by influencing
their employment choices.
12
Liu, J. and Wang, T.
The Effects of Internet-Using on Farmer Employment Choice and Income Differentiation: An Empirical Study Based on the CGSS2017.
DOI: 10.5220/0012069200003624
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2022), pages 12-17
ISBN: 978-989-758-658-3
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESES
2.1 Internet Using and Farmer Income
Differentiation
With the continuous improvement of broadband and
other network infrastructure, the accessibility of
Internet using has been greatly improved in rural
residents (Luo and Liu, 2022), Internet technology
has become an important factor in farmers
production and life. In Solo's economic growth
model, the production factors are mainly divided
into capital (K) and labor (L). Internet technology is
added to the model as "technology development
level (A)"(Zhu et al, 2022). In the rural economy,
the use of Internet technology can not only help the
farmer to quickly capture the trading information of
agriculture, reduce transaction costs due to
information asymmetry, and improve income
opportunities. At the same time, it can effectively
improve the information access efficiency of the
rural labor market, reduce the cost of finding jobs
(Ma et al, 2022), and improve the opportunities for
rural surplus labor to engage in non-agricultural
employment, thereby increasing income. However,
for some people who are not good at using Internet
technology, or even do not use Internet technology,
they have lost many opportunities and ways to
improve their income because the less information
(Liu and Han, 2018), and have limited access to
Internet technology premiums (Zhang, 2022), so the
income gap between them and farmers who use
Internet technology is more growing. Based on this,
the first hypothesis is proposed. H1: Internet using
aggravates the income differentiation of farmers.
2.2 The Role of Employment Choice
The employment choice is closely related to the
income differentiation of farmers. For agriculture
farmers, they can timely obtain agricultural
information by using Internet, such as land
circulation and agricultural products trading, and
improve agricultural production efficiency. In
addition, "Internet plus" products, such as Internet
finance, can accelerate the digital transformation of
rural industries and reduce information transaction
costs, thus promote financial support for industrial
development (Li et al, 2021). For non-agricultural
farmers, the Internet is not only a tool that can
improve productivity, but also an important means
to expand social capital (Ma and Ning, 2017). By
using Internet, they can obtain tremendous labor
market information, broaden the scope of
employment and increase employment opportunities.
For some entrepreneurial farmers, the rural e-
commerce industry provides a platform for them to
start their own businesses, which benefits are greater
than employment (Song and He, 2021). Whether for
agricultural farmers, non-agricultural farmers or
entrepreneurial farmers, the use of Internet is not
significantly beneficial. Farmers of different ages,
educational backgrounds and family backgrounds
have different Internet using skills and information
identification capabilities. Farmers who with higher
education and are good at using Internet technology
often choose a suitable job; farmers who with low
educational background and are not good at using
Internet technology cannot choose useful
information or even indulge in Internet games, thus
aggravating the income gap of farmers. Based on
this, the second hypothesis is proposed. H2: Internet
using aggravates the income differentiation of
farmers by influencing their employment choices.
3 DATA AND METHODS
We use the OLS model and Stata16 software to
estimate the impact of Internet using on income
differentiation. The specific model is as follows:
11 2 1
Income nternet ontrolsIC
α
ββ
ε
=+ + +
(1)
Secondly, in order to test the meditation effect of
employment choice, this paper refers to the
meditation test method of Wen et al (2004), and on
the basis of formula (1), are further added (2) and (3)
to build the meditation effect model:
21 2 2
Employment nternet ontrolsIC
α
γγ
ε
=+ + +
(2)
31 2
33
Income nternet Employment
ontrols
I
C
αδ δ
δε
=+ + +
+
(3)
Above (1) ~ (3), controls including gender, age,
education, health, political status, marital status,
social security, family size, region,
α
is constant,
βγ
δ
、、
are variable regression coefficients,
ε
is
the error item.
The Effects of Internet-Using on Farmer Employment Choice and Income Differentiation: An Empirical Study Based on the CGSS2017
13
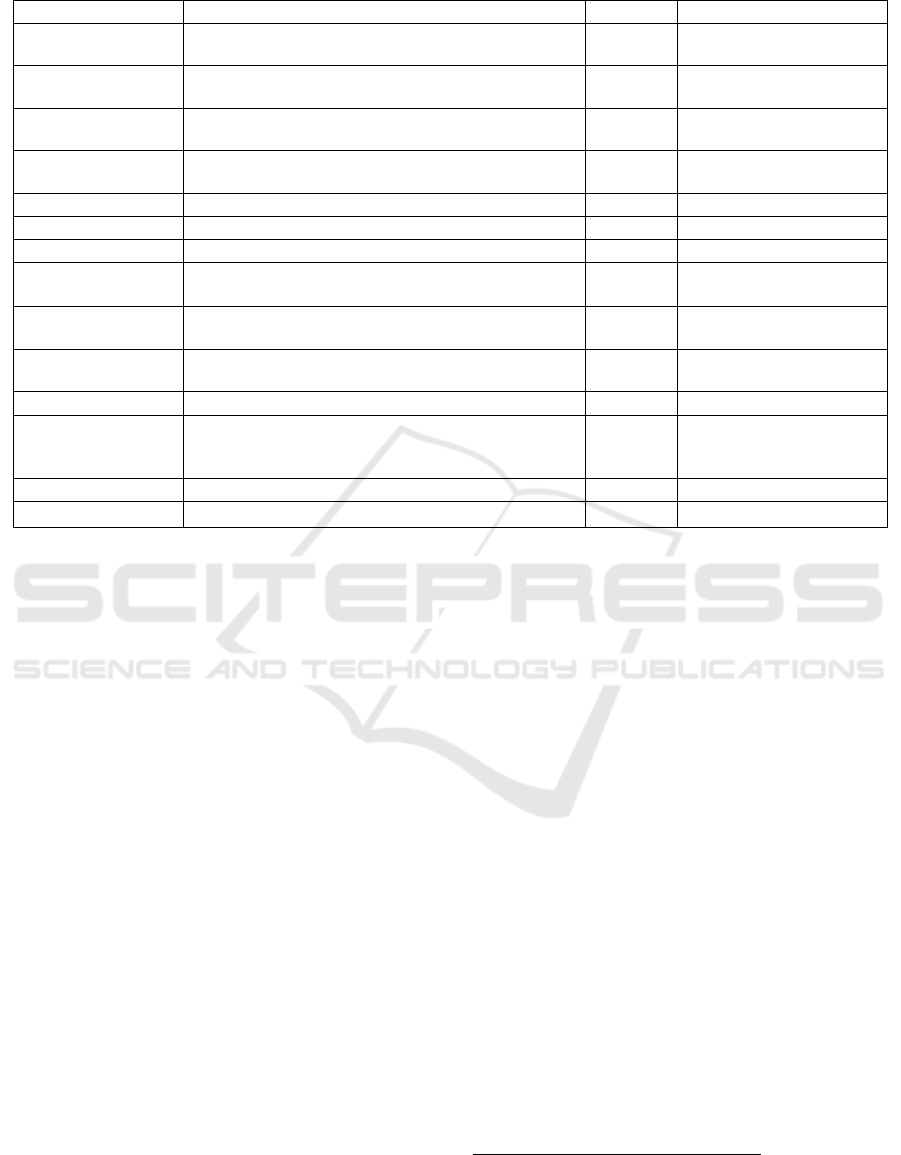
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of the variable.
Variable name Variable assignment Mean Standard deviation
Annual gross
income
Personal total income for last year (2016) (log
value
)
4.207 0.539
Annual labor
income
Occupational / labor income for last year (2016)
(
lo
g
value
)
4.219 0.531
Internet using
Whether to use the Internet (ever used =1, not used
=0)
0.580 0.494
Employment
choices
Non-agriculture employment =1, farming or
unem
p
lo
y
ed =0
0.480 0.500
Employment types Entrepreneurial =1, migrant =2, other =0 1.825 0.380
gender Male =1, female =0 0.530 0.499
age Actual age (using 2017 minus birth year) 45.950 12.255
Education level
No education =1, primary school =2, middle school
=3, high school=4, junior college or above =5
0.550 1.407
Health condition
Very unhealthy =1, compared unhealthy =2,
generally =3, compared healthy =4, very healthy =5
3.530 1.106
Political status
Communist Party member =1, non-Communist
Party member =0
0.910 0.283
Married Married =1, unmarried, divorced, or widowed =0 0.830 0.372
Social security
The following insurance conditions add: endowment
insurance or medical insurance, participation =1, not
p
articipation =0
1.750 0.752
Family size Number of family members 3.090 1.559
Region Region: East =1, central =2, west =3, northeast =4 2.210 1.018
We use the Chinese General Social Survey 2017
(CGSS 2017) data to investigate the possible impact
of income differentiation on internet using. The
survey adopts multi-stage stratified probability
sampling design, consisting of 28 provinces regions
nationwide. The CGSS data particularly suits the
analytical needs of this study because it includes
variables on income, working and so on. According
to the research needs, we retained the household
registration status of "agricultural registration and
residence household registration (formerly
agricultural registration)" and the age of 18 to 65
samples; while excluding in the current school stage,
obtained through the entrance to non-agricultural
registration and related variable information
seriously missing samples, leaving in 4527 samples.
Income differentiation, the key dependent
variable, is measured by annual total income and
annual labor income. Individual annual income is
measured by "individual total income of the whole
year last year (2016)", and annual labor income is
measured by "individual occupational/labor income
of the whole year last year (2016)". In order to
prevent the results due by the heteroscedastic
problem (Ma et al, 2022), the paper takes the log
value of income. The key independent variable,
internet using, is measured by the questionnaire
"Your use of Internet in the past year" According to
the existing research, we use the binary variables to
measure the Internet using.
2
①
The mediation variable
is employment choice, which is divided into three
forms: non-agricultural employment, farming and
unemployed. According to the item of "your current
work experience", engaged in non-agricultural
employment is assigned value of 1, and the farming
or unemployed individuals is 0. In addition, non-
agricultural employment is further divided into two
forms: employer or self-employment and employee.
Usually, the former is considered as entrepreneurial
employment, while the latter is considered as
migrant employment.
Considering that farmers employment choice and
income differentiation are also affected by other
factors, we add some control variables referring to
previous studies (Zhu et al, 2022; He et al, 2022),
including gender, age, education level, health
condition, political status, married, social security,
family size and other variables. In addition,
considering the possible differentiation in Internet
using among farmers in different regions, we were
introduced into the regional virtual variables,
divided into eastern, central, western and northeast
regions. Specific description of each variable and the
descriptive statistical results are shown in Table 1.
2
"Never use the Internet" is assigned value of 0, as well as
"few", "sometimes", "often" and "frequent" use the
Internet are assigned value of 1.
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
14

4 EMPIRICAL RESULTS
4.1 Benchmark Regression
We use Stata16 software to analyze data and test
model. In table 2, model (4) and (8) report the
estimated results of the impact of Internet using on
farmers income differentiation. The regression
coefficient for the effect of Internet using on
individual total income was 0.298, and the
regression coefficient for the impact of labor income
was 0.288. The regression results show that the
Internet using has a positive impact on farmers
income, and is significant at the statistical level of
1%, which shows that the use of Internet is helpful
to improve farmers income. However, the
differentiation in the effect of the two incomes is
small. The reason for that the study sample is mainly
the farmer labor force, and their total income mainly
include the labor income. In addition, education
level, health conditions and social security have a
significant positive impact on farmers income.
Which indicates that individuals have more
opportunities and ways to obtain income and are
more likely to increase their income with the higher
education level, the better health and involved in
social security. The coefficient of gender and
married was also significantly positive, indicating
that married individuals had higher income than
unmarried, and male individuals earn more than
females. However, the coefficient of the influence of
age, political status, family size and regional
differentiation on farmers income is negative. With
the increase of age, the decrease of farmers income.
Compared with the central and western regions,
farmers in the eastern economically developed
regions have more advantages in increasing income.
The above empirical results test hypothesis 1.
4.2 The Meditation Effect of
Employment Choice
The impact of Internet using on farmers income
differentiation has been tested, so what mechanism
does Internet using affect farmers income
differentiation? In table 2, model (1) shows that
Internet using has a significant positive impact on
employment choice, indicating that Internet using
can promote non-farm employment. Secondly,
further add employment choice in Internet using
impact on income model, in table 2, model (5)
shows that the influence of the Internet using on the
farmers income still has a significant positive impact
(coefficient from 0.298 to 0.222), and the
employment choice has a significant positive impact
on farmers income. According to the meditation
effect of testing ways, employment choice plays a
partial meditation role in the relationship between
Internet using and farmers income differentiation,
and the meditation effect is 7.61%.
In order to make a more comprehensive analysis,
we divide the non-agricultural employment into
entrepreneurial and migrant employment. In table2,
model (2) and (3) show that Internet using has a
positive impact on entrepreneurial and a negative
effect on migrant employment. The possible reason
is that entrepreneurial farmers have a higher demand
for the Internet. With the development of
agricultural technology and e-commerce, commodity
production and sales need Internet. Thus Internet
may encourage farmers to find more opportunities to
entrepreneurship. On the contrary, migrant work has
low demand for Internet so that inhibiting the choice
of migrant employment. Secondly, in the table 2,
model (6) and (7) show that the Internet using still
has significant positive impact on income. And
entrepreneurial has a significant positive impact on
income but migrant employment has significant
negative impact on income. Above, it can be seen
that entrepreneurial and migrant employment play a
meditation role in the relationship between Internet
using and income differentiation.
3
①
The meditation
effect is respectively 0.91% and 0.95%. Based on
the above, hypothesis 2 supported.
3
In addition, the results with the annual labor income as
the dependent variable are consistent with the above
conclusions, and the specific results are not listed due to
the extent limited.
The Effects of Internet-Using on Farmer Employment Choice and Income Differentiation: An Empirical Study Based on the CGSS2017
15
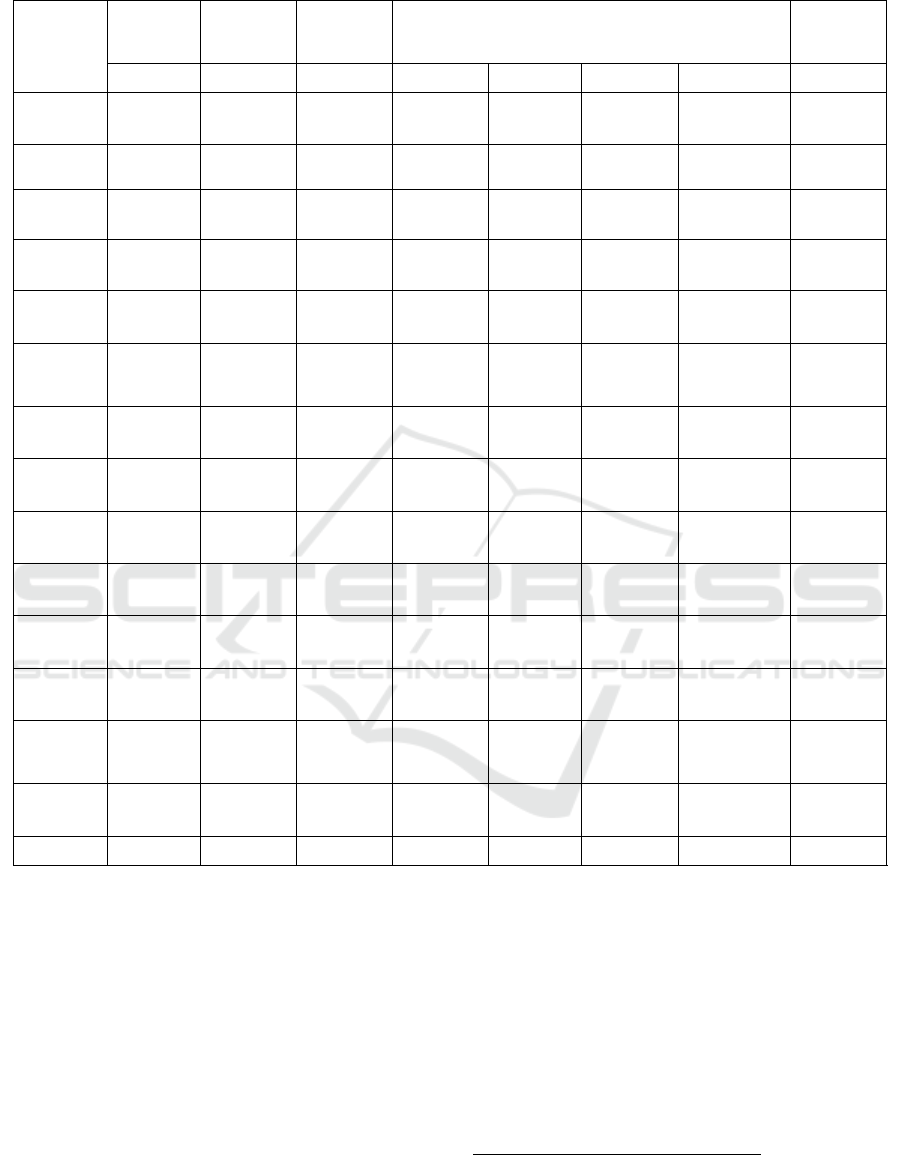
Table 2: Mechanistic analysis of the impact of Internet using on farmers income differentiation.
variable
EC EE ME Annual gross income
Annual
labor
income
(1) (3) (5) (4) (2) (4) (6) (8)
Internet
using
0.234***
(0.016)
0.088**
(0.028)
-0.106***
(0.029)
0.298***
(0.017)
0.222***
(0.016)
0.138***
(0.021)
0.138***
(0.021)
0.288***
(0.017)
EC
0.325***
(0.015)
EE
0.104***
(0.016)
ME
-0.090***
(0.016)
Gender
0.090***
(0.013)
-0.003
(0.020)
0.013
(0.020)
0.199***
(0.013)
0.170***
(0.013)
0.144***
(0.015)
0.144***
(0.015)
0.214***
(0.013)
Age
0.008***
(0.001)
0.001
(0.001)
-0.002*
(0.001)
-0.007***
(0.001)
-
0.004***
(0.001)
-0.004***
(0.001)
-0.004***
(0.001)
-0.008***
(0.001)
Education
level
0.028***
(0.005)
-0.020**
(0.006)
0.014*
(0.006)
0.040***
(0.005)
0.031***
(0.005)
0.037***
(0.004)
0.036***
(0.004)
0.036***
(0.005)
Health
condition
0.056***
(0.006)
-0.007
(0.011)
0.007
(0.011)
0.082***
(0.006)
0.063***
(0.006)
0.044***
(0.008)
0.044***
(0.008)
0.077***
(0.007)
Political
status
-0.065*
(0.023)
0.085**
(0.030)
-0.062*
(0.031)
-0.054*
(0.024)
-0.033
(0.023)
-0.033
(0.023)
-0.029
(0.023)
-0.058*
(0.025)
Married
0.025
(0.018)
0.118***
(0.028)
-0.114***
(0.029)
0.122***
(0.019)
0.114***
(0.018)
0.084***
(0.021)
0.086***
(0.021)
0.117***
(0.02)
Social
security
0.004
(0.009)
0.016
(0.012)
-0.016
(0.012)
0.057***
(0.009)
0.056***
(0.008)
0.069***
(0.009)
0.069***
(0.009)
0.058***
(0.009)
Family
size
-0.002
(0.004)
-0.001
(0.006)
-0.001
(0.007)
-0.014**
(0.004)
-0.013**
(0.004)
-0.015**
(0.005)
-0.015**
(0.005)
-0.018***
(0.004)
Region
-
0.093***
(
0.006
)
0.045***
(0.01)
-0.056***
(0.010)
-0.086***
(0.007)
-
0.056***
(
0.006
)
-0.080***
(0.007)
-0.080***
(0.007)
-0.085***
(0.007)
Constant
0.717***
(0.060)
-0.057
(0.088)
1.117***
(0.090)
4.029***
(0.062)
3.797***
(0.059)
4.270***
(0.066)
4.364***
(0.068)
4.110***
(0.064)
R
2
0.313 0.043 0.044 0.371 0.433 0.259 0.255 0.378
Note: EC=Employment Choice, EE= Entrepreneurial Employment, ME= Migrant Employment;
*** p <0.01, ** p <0.05, and * p <0.1
4.3 Robustness Test
To ensure the robustness of the estimated results, we
replace variables to test. First, the regression takes
the information source and Internet using frequency
as independent variables. The information source is
measured "Is the main source of information the
Internet (including mobile Internet)", and Internet
using frequency treated as 1-5. In table 3, models (1)
and (2) show that the Internet as the main source of
information significantly increases the farmers and
Internet using frequency will increase the income.
Secondly, the logarithm of family annual income
was used as the dependent variable. In table 3,
model (5) shows that the coefficient of Internet
using is still positive, that is, Internet using improves
family annual income. In addition, select the youth
subsample to analysis
4
①
. In table 3, models (3) and
(4) show that Internet using improves the income
level of young farmers. Thus, the above results have
strong robustness.
4
According to the UN WHO age classification criteria in
2013, the sample who was under 44 years was defined as
youth.
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
16
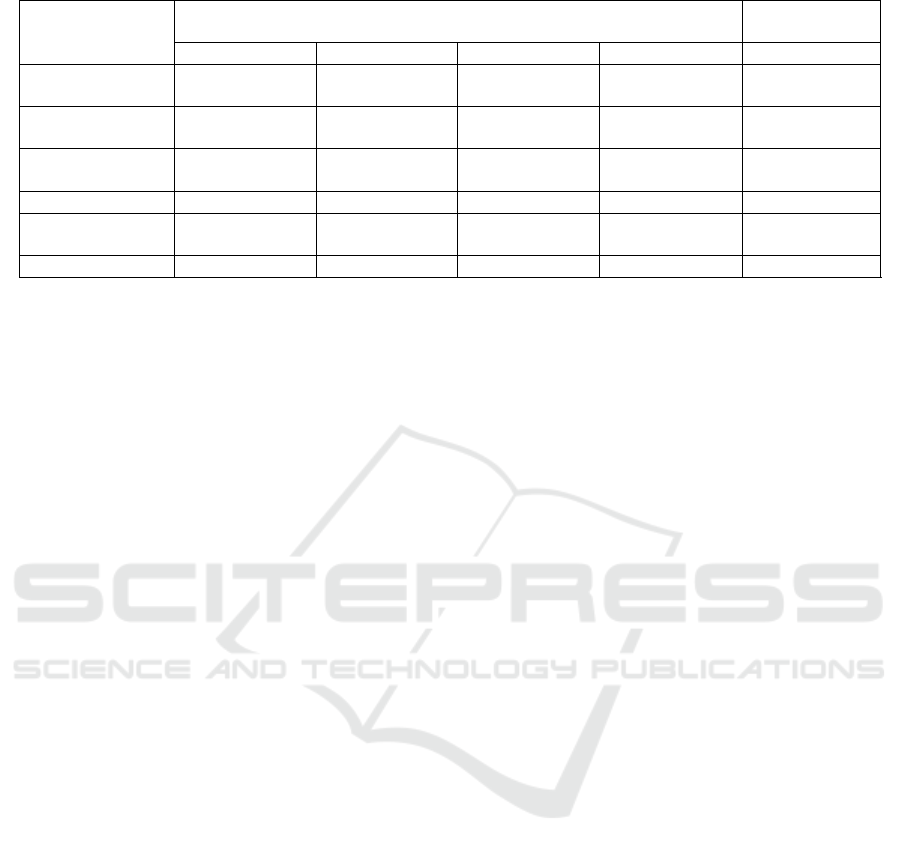
Table 3: Effect of the effect of table replacement variables on farmers income differentiation.
variable
Annual gross income
Family annual
income
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
Internet using 0.294***(0.032)
0.208***
(
0.027
)
Information
sources
0.057**(0.023)
Frequency of
Internet using
0.092***(0.005)
0.085***(0
.008)
Control variable Control Control Control Control Control
Content 4.463***(0.060) 3.901***(0.065) 3.979***(0.090) 3.833***(0.093)
4.651***
(0.099)
R
2
0.324 0.370 0.302 0.313 0.168
Note: ***
p
<0.01, **
p
<0.05, and *
p
<0.1
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper uses OLS multiple regression and Stata16
software to analyze data in order to examine the
Internet using impact on farmers income
differentiation. The empirical results show that:
Internet using promote the farmers income
differentiation. By using the Internet, the income
level of farmers significantly increased by 0.298
than not use the Internet. Second, Internet using
promotes farmers non-agricultural employment to
increase their income such as information and
communication technologies, and employment
choice plays a meditation role in the process. In the
further subdivision of non-agricultural employment,
Internet using positively affects entrepreneurial such
as providing technical support for entrepreneurship,
but has a negative impact on migrant employment.
Increasing farmers income is the focus of
"agriculture, rural areas and farmers" in China and to
achieve common prosperity. The popularization of
the Internet has provided more opportunities to
increase farmers income, but there are still a
considerable number of farmers who cannot enjoy
the digital dividend due to their own conditions.
Therefore, the government should improve the
construction and upgrading of rural network
infrastructure, strengthen the information skills
training of farmers, so that more low-income
farmers can participate in the digital economy.
Meanwhile, promoting non-agricultural employment
is an important way to increase farmers income,
narrow the gap between urban and rural areas, and
accelerate the process of urbanization. We should
promote the linkage between digital technology and
the factor market, provide services for farmers to
participate in non-agricultural employment through
the Internet, and promote the continuous increase of
farmers income.
REFERENCES
He, Q. Y., Liu, G. Q., Zou, X. Y. (2022). Effect of Internet
use on employment choice of rural labor: An Empirical
Study Based on Formal and Informal Employment.
Journal of Agro-Forestry Economics and Management,
21, 385-394.
Li, J. R., Shen, Y., Yang, J., Chen, B. L. (2021). Research
on the impact of Internet finance use on farmers'
multidimensional poverty reduction. Statistics and
Information Forum, 36,104-118.
Liu, X. Q., Han, Q. The impact of rural residents' Internet
use on their income and its mechanism - based on the
China Household Tracking Survey (CFPS) data.
Agricultural Technology and Economy, 123-134.
Luo, M. Z., Liu, Z. Y. (2022). Internet use, social identity
and rural residents' Happiness. China Rural Economy,
114-131.
Ma, S. Z., Wu, P., Pan, G. J. (2022). Internet use, consumer
service industry expansion and labor income
differentiation. Economic Perspectives, 68-84.
Song, L., He, Y. (2021). Research on the impact of Internet
use on China's urban and rural family entrepreneurship.
Science of Science Research, 39,489-498.
Wen, Z. L., Zhang, L., Hou, Ji. T., et al. (2004). Testing
and application on of the mediating effects.
Psychological Journal, 614-620.
Zhang, Z. Q. (2022). Internet use and income inequality of
farmers. Economic Journal, 39, 45-54.
Ma, J. L., Ning, G. J. (2017). The Internet and non farm
employment of China's rural labor. Financial Science,
50-63.
Zhu, S. B. , Xiong, F. X., Zhu, J. (2022). Impact of
Internet use on rural households' income: An analysis
of the mediating effect based on social capital. Journal
of Agro-Forestry Economics and Management, 21,
518-526.
The Effects of Internet-Using on Farmer Employment Choice and Income Differentiation: An Empirical Study Based on the CGSS2017
17
