
Comparative Study on Statistical Measurement and Regional
Differences of Chinese Public Governance Efficiency
Huimin Han
*a
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
Keywords: Efficiency of Public Governance, Stochastic Frontier Production Function, Technical Efficiency, Decision
Tree Algorithm.
Abstract: Based on the provincial panel data from 2007 to 2020, this paper uses the translogarithmic stochastic
frontier function (SFA) to measure the main influencing factors of China's public governance efficiency and
the technical efficiency of public governance output under the same production frontier. Studies show that
since the 18th CPC National Congress, the efficiency of China's public governance has been continuously
improved; There are significant differences in the technical efficiency of public governance among regions.
The technical efficiency of eastern and western regions decreases successively, but the efficiency of central
and western regions increases obviously. According to the efficiency and input level, the influence of
human input, expenditure structure, government scale, urbanization rate and other factors is more
significant. The quadruple decomposition of total factor productivity shows that the technical efficiency and
scale efficiency of public governance have a huge space for improvement. Further combining the decision
tree algorithm, the urbanization level as one of the nodes to classify our county level government to prove
the impact of urbanization on the efficiency of public governance.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
The Third Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central
Committee put forward the overall goal of
deepening the reform in an all-round way, which is
to "promote the modernization of the national
governance system and governance capacity".
Correspondingly, the research in the field of public
administration focuses on the field of governance,
and the research topic of public administration has
gradually shifted from public management to public
governance (Wen, 2018). As a super large
organization in national governance, the government
is relative to or even higher than the market
mechanism, which is related to the resource
allocation efficiency of the whole society.
At present, the academic circle mainly uses DEA
method to measure the efficiency of public
governance of our country. Some typical research
results include: He Baocheng et al. measured
governance efficiency based on the three-stage
DEA-BBC model under input guidance, and
believed that government governance efficiency has
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8981-6166
positive spatial spillover effect, which can be
transmitted between neighboring regions through
"learning effect" and "demonstration effect", thus
promoting the improvement of regional overall
governance efficiency (He Baocheng et al.,2021).
Zhang Jiyuan was specific to the field of public
security governance, and made an in-depth analysis
of the technical efficiency of public security
governance expenditure in Sichuan Province. The
results show that factors such as urbanization level
and local per capita public financial revenue have a
significant impact on the efficiency of public
security governance (Guo et al.,2021). Some
scholars also use government governance efficiency
as an intermediary variable to analyze the impact of
institutional reform. For example, Guo Mengnan et
al. empirically tested the impact of audit
management system reform on the growth of total
factor productivity and the intermediary role of
government governance efficiency. Studies have
found that the reform of audit management system
can improve the total factor productivity by
improving the government's anti-corruption efforts
(Zhang, 2020). Therefore, in order to enhance the
scientificity and comprehensiveness of efficiency
Han, H.
Comparative Study on Statistical Measurement and Regional Differences of Chinese Public Governance Efficiency.
DOI: 10.5220/0012070700003624
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2022), pages 105-113
ISBN: 978-989-758-658-3
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
105

evaluation, it is necessary to reflect on the whole and
part based on the concept of "total factor
productivity" improvement, and construct an input-
output index system of public governance efficiency
evaluation with environmental regulation as the link
and evaluation dimension as the unit.
However, from the perspective of research
methods, the evaluation based on DEA method has
certain limitations, that is, the efficiency of DEA
evaluation measure is relative and susceptible to the
influence of outliers, and all random interference
items are also included in the technical inefficiency.
This means that other research methods should be
comprehensively applied to make up for the
deficiency of DEA method in further study on the
efficiency of public administration. Different from
DEA method, the biggest advantage of SFA method
is that the influence of random factors on output is
considered by dividing random interference factors
into technical inefficiency and random error terms.
2 THEORETICAL MODEL AND
DATA
2.1 Stochastic Frontier Model
The technical efficiency measurement method of
stochastic frontier model was first proposed by
Farrel in 1957, which mainly analyzes the efficiency
from two parts: scale efficiency and pure technical
efficiency. After the development and improvement
of Aigner, Meeusen, Forsund, Schmidt and many
other scholars, it has become one of the most
commonly used methods to measure technical
efficiency at present. The stochastic frontier analysis
model is used to estimate the production function. Its
basic expression is:
Y
=
f
(x
;t)exp(
v
−u
)
(1)
In formula (1),Y
represents the actual output of
sample i at time t; f () represents the optimal output
that can be achieved under the condition of existing
technological progress;x
represents the factor input
vector of sample i at time t;v
and u
represents the
random error term and technical inefficiency index
of sample i in the production process at the time of t.
Battese and Coell further (BATTESE et al., 1992)
proposed a stochastic frontier production function
for panel data estimation, and its model form is as
follows:
Y
=X
β+(V
+U
)
(2)
V
as a random error term, it is the
uncontrollable factors in the sample management
process, such as emergencies, geographical factors,
statistical errors, etc., which may affect the
production. Since the direction of the influence
cannot be determined, the random error term is set
as the bilateral error term, i.e V
~N(0,σ
).At the
same time,V
is independent of U
=(U
exp(−η
(t − T))).η is the parameter to be estimated.u
is
the technical inefficiency of sample i in period
t. u
=N
(m
,σ
), m
=Z
δ , u
follows a
semi-normal distribution and is a non-negative
random variable.m
is the technical loss function.Z
is the vector group composed of exogenous variables
affecting the efficiency loss of sample i.δ is also a
parameter to be estimated. σ
and σ
as an
argument,the variance of the term conforming to the
residual is σ = σ
+ σ
.To define γ =
σ
/σ
+ σ
(0 ≤ γ ≤1). U
is the management
error term, which refers to the distance between the
sample output and the production possibility
boundary. Only when there is no management error
in the input and the technical level reaches the
optimal condition(U
=0),the output is going to
be on the frontier. At the same time, under the
influence of many factors, such as the failure of
public governance, the level of government
governance and the effectiveness of technology,
technology loss is common in the process of public
governance. So let's assume U
follows a truncated
normal distribution , U
~N(μ
,σ
μ
),The mean
of administrative error is μ
,reflect the technical
efficiency loss accordingly.
The frontier production function is obtained
based on regression, which can calculate the
production technical efficiency (TE) and efficiency
loss ( μ
) of each sample public governance
process.Thus, the factors affecting the efficiency
loss of public governance are analyzed, among
which:
TE
=
E(
Y
|μ
,X
)
E=(
Y
|μ
=0,X
)
(3)
The numerator to the right of formula
(3),E(Y
|μ
,X
)is the actual total output of the
sample, and the denominator is the maximum
possible output given the input level.TE
is the ratio
of the two, and it ranges from 0 to 1. The closer it is
to 0, the higher the technical efficiency loss is. The
closer it is to 1, the higher the technical efficiency.
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
106

μ
=δ
Z
+δ
(4)
μ
is the technical loss value of each sample
calculated above, reflecting the difference between
the input level and the optimal technical level of the
sample in the process of public governance; Z
represents the k-th variable that affects the technical
loss value; δ
is the parameter to be
estimated,reflect the influence of variables on
technical loss.When the coefficient is negative, it
indicates that the variable has a positive influence on
the technical efficiency, while the opposite indicates
that the variable has a negative influence; δ
represents a random variable subject to an extreme
distribution.
In general, due to the flexible form of the
translogarithmic production function, the model can
reflect the combined influence of different input
factors on the output in the production function, and
its output elasticity can reflect the differences in the
technological progress of different inputs, relax the
strict assumption of technological neutrality, and
further reveal more characteristics of the system.
Therefore, this paper intends to adopt a time-varying
efficiency stochastic frontier production model in
the form of translog of the following three input
factors:
ln
Y
=β
+β
(ln
K
)+β
(lnL
)
+β
(lnE
)+β
t
+β
(lnK
lnL
)
+β
(lnK
lnE
)
+β
(lnL
lnE
)
+β
(lnK
)
+β
(lnL
)
+β
(lnE
)
+β
t
+β
(lnK
)t
+β
(lnL
)t
+β
(lnE
)t +
v
−u
(5)
In the model, Y is the public governance output
of i province in the t year.β
、β
、β
、β
、
β
are the parameter vector to be estimated. Use
time trend t to reflect technological progress; X is
the input factor, and K, L and E are the capital, labor
and resource input respectively.
According to theoretical model (4), the
influencing factor model of technical loss is also set:
μ
= δ
+ δ
go
v
+ δ
cit
+ δ
gdp
+ ω
(6)
μ
is the technical loss in the public governance
process of i province in the t year. The influencing
factors of public governance technology loss can be
divided into internal causes and external causes. The
internal causes are mainly related to the basic
objective conditions related to public governance,
while the external causes are mainly the regional
economic development level that affects the output
of public governance. In the selection of specific
variables, this paper selects three types of
influencing factors, using government size (gov) to
reflect the natural conditions of public governance
output, and urbanization rate (cit) and per capita
GDP (gdp) to reflect the technical conditions of
public governance output.
2.2 Selection of Data and Variables
2.2.1 Data Selection and Source
Since the 18th CPC National Congress, national
governance has become the focus of public
management research, and the efficiency of public
governance has become an important tool to
promote the reform of public governance. The
government has gradually strengthened supervision
over the exercise of power, increased input in areas
related to people's livelihood, assumed more
responsibilities for social development, and
committed itself to providing better public services.
Great achievements have been made in the
modernization of the national governance system
and capacity, and in comprehensively deepening
reform. Therefore, this study selected the public
governance input and output data of 31 provinces
and autonomous regions except Hong Kong, Macao
and Taiwan from 2007 to 2020. Among them, the
basic data come from the statistical yearbooks of
provinces of China over the years, and the indicators
that cannot be directly obtained are shown in Table 1.
2.2.2 Variable Selection and Processing
The selection of input indicators, specifically for
public governance, refers to the practice of Qi Yu et
al., which correspond to three types of indicators:
financial resources, human resources and material
resources. Output indicators refer to the research
results of some scholars and take governance in
related fields as a dimension to measure the output
intensity of public governance. According to the
research of Beijing Normal University on local
government efficiency, the relevant projects of
Beijing's fiscal expenditure structure, which ranks
first in government efficiency, are screened.
Considering the availability of data, indicators in
Comparative Study on Statistical Measurement and Regional Differences of Chinese Public Governance Efficiency
107

science and technology are selected to show the
output of economic development capacity. The
output reflecting the provision of public goods was
measured by the two indicators of education and
health, and the output reflecting the socio-economic
welfare and equity of residents was measured by the
inverse of social security and employment and the
Engel coefficient and Gini coefficient of residents.
The indexes of environmental protection,
agricultural development and transportation are used
to reflect the output of economic activity basis and
environment. The output value is obtained by
logarithmic sum of the above indexes and is used as
the explained variable in the stochastic frontier
production function model. The input and output
indicators of public governance efficiency set in this
study are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Input and output indicators of public governance efficiency measurement.
Indicator Meanin
g
Method of measurement
Index of
input
K (Capital - financial power) Per capita fiscal expenditure
L (Labor – Manpower) Employment in public administration, social
security and social organizations per 10,000
people
E (Resources - Material
resources
)
Per capita state fixed asset investment
Indicators of
output
Economic development
capacity: Science and
technolo
gy
Authorized number of domestic patent
applications per 10,000 people
Public goods provided:
education
(Primary school teacher ratio + junior school
student teacher ratio) /2
Number of beds in medical and health
institutions per 1,000 population
Resident welfare and equity
Number of people per 10,000 participating in
unemployment insurance at the end of the year
The inverse of the Gini coefficient and the
Engel coefficient
Foundation of Economic
activity and environment
Wastewater discharge per unit of GDP
Per capita disposable income of rural residents
(Railway + highway mileage)/Land area of
each province
3 ESTIMATE RESULTS
3.1 Analysis of Model Estimation
Results
Stata16.0 software was used for regression analysis
of model (5) and model (6) to estimate the
influencing factors of input-output stochastic frontier
production function and technical efficiency in the
process of public governance. The estimated results
are shown in Table 2 and Table 3 respectively.
According to σ
and σ
, can figure out that the γ
coefficient is 0.9586.It shows that the variance of
technical inefficiency contributes the most to the
fluctuation of the whole public governance output,
that is, the technical inefficiency item cannot be
ignored. At the same time, it also shows that the
variance of technical inefficiency can explain 95%
of the total variance of the whole model. It can be
seen that the setting of stochastic frontier function
model is reasonable. η is greater than 0 and
significant at 1%, indicating that it is acceptable that
the technical efficiency of public governance will
change over time. According to chibar2, the P value
of 0.0000 rejects the null hypothesis at the 1% level
H
"There are no inefficiencies". That is, there is an
inefficiency term.
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
108
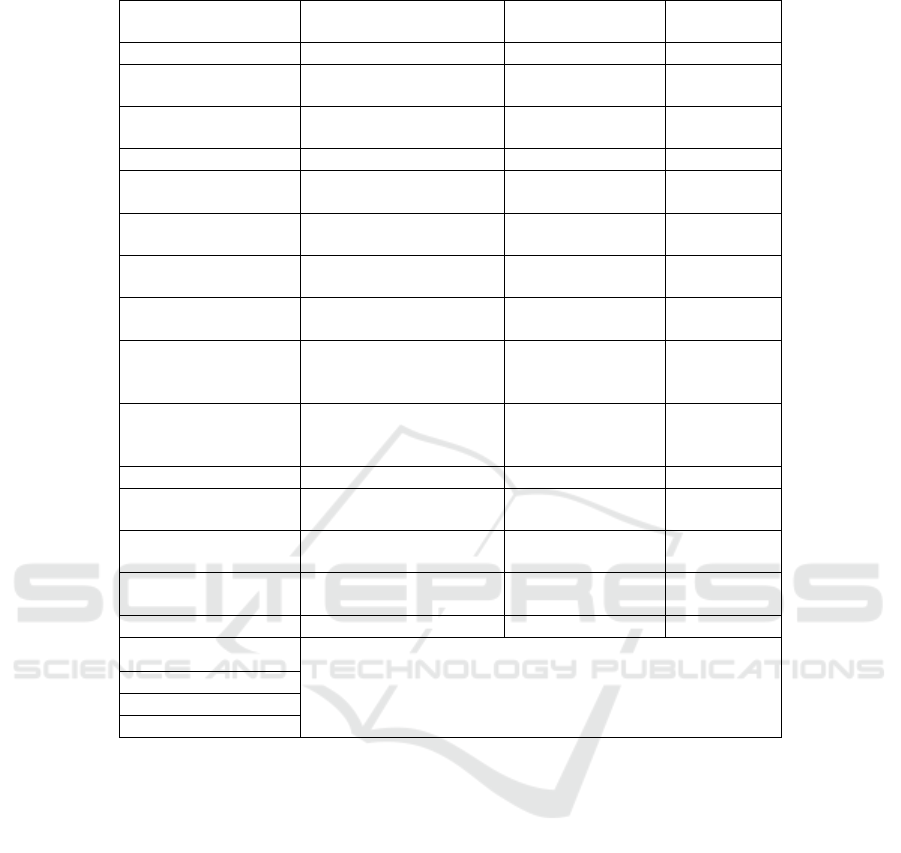
Table 2: Regression results of input-output stochastic frontier production function in public governance process.
variable Coefficient of
estimation
Standard
deviation
Z test
Financial input -0.3706 0.4966 -0.75
Input of
man
p
owe
r
0.1035* 0.0531 1.95
Input of material
resources
-0.6635* 0.3371 -1.97
Term of time 0.1927** 0.0756 2.55
Quadratic term of
financial resources
-0.0122 0.0241 -0.51
Manpower
secondary ter
m
-0.0053 0.0049 -1.06
Quadratic
material ter
m
0.0080 0.0292 0.27
Time quadratic
ter
m
-0.0014** 0.0005 -2.68
Financial
resources ×
man
p
owe
r
0.0011 0.0075 0.15
Financial
resources × material
resources
0.0653 0.0451 1.45
Man × material -0.0150** 0.0046 -3.25
Financial
resources x time
-0.0007 0.0061 -0.11
Manpower ×
time
0.0025** 0.0008 3.13
Material
resources x time
-0.0070 0.0049 -1.43
Term of constant 13.40607*** 2.2081 6.07
σ
0.0028
0.0667
0.9586
0.0145***
σ
γ
η
Note: *, ** and *** are significant at the level of 10%, 5% and 1% respectively.
The technical efficiency of public governance in
each province was measured under the same
production frontier (Table 3). From the perspective
of the total samples: first, the average technical
efficiency of public governance in each province
keeps improving, and the average of total samples
rises from 0.4510 in 2007 to 0.5132 in 2020.
However, the standard deviation of the total sample
over the years decreased steadily from 0.1649 to
0.1510, indicating that the technical efficiency of
public governance in various provinces gradually
converged and the differences between provinces
were decreasing. Second, in 2020, the average of the
technical efficiency of public governance in all
provinces is 0.5132. There are still relatively large
losses of technical efficiency in Chinese public
governance. Combining the measurement results of
Table 3, we can find that the loss of technical
efficiency of public governance mainly comes from
management errors, that is, the technical efficiency
of public governance will be further increased if we
can better allocate factor resources or improve the
management level pertinately in the process of
public governance. Thirdly, take the 18th National
Congress as the time node to plot the change of
provincial average public governance technical
efficiency. From the perspective of time dimension,
the total factor productivity of public governance in
western China has the fastest growth rate. The
growth of total factor productivity of public
governance in eastern China is relatively flat. From a
national perspective, the western regions such as
Ningxia, Xizang and Xinjiang, central provinces
such as Henan, Hubei and Jilin, as well as the
eastern provinces such as Guangdong and Guangxi,
where the efficiency of public governance
technology is relatively low, have a more obvious
growth rate, while Shanghai, Beijing and Zhejiang
Comparative Study on Statistical Measurement and Regional Differences of Chinese Public Governance Efficiency
109

have a smaller growth rate. In terms of the specific
period, since the 18th CPC National Congress, the
efficiency of public governance in all provinces has
steadily improved, and the efficiency of public
governance in central and western regions has
significantly improved.
Table 3: Total samples and comparative analysis of
technical efficiency of public governance in eastern,
central and western China from 2007 to 2020.
year Total sample size
Mean Standard
2007 0.4510 0.1649
2008 0.4558 0.1639
2009 0.4607 0.1629
2010 0.4655 0.1618
2011 0.4703 0.1608
2012 0.4751 0.1597
2013 0.4799 0.1586
2014 0.4847 0.1576
2015 0.4895 0.1565
2016 0.4943 0.1554
2017 0.4990 0.1543
2018 0.5038 0.1532
2019 0.5085 0.1521
2020 0.5132 0.1510
Mean 0.4822
Central Region
Mean Min Max
0.4146 0.3733 0.4784
0.4198 0.3786 0.4835
0.4252 0.3840 0.4886
0.4304 0.3893 0.4937
0.4357 0.3947 0.4987
0.4409 0.4000 0.5038
0.4461 0.4053 0.5088
0.4513 0.4106 0.5138
0.4565 0.4160 0.5187
0.4617 0.4266 0.5237
0.4669 0.4213 0.5286
0.4721 0.4266 0.5335
0.4772 0.4318 0.5383
0.4823 0.4371 0.5432
0.4486 0.4424
Western Region
Mean Min Max
0.3355 0.2649 0.4047
0.3407 0.2700 0.4100
0.3406 0.2752 0.4153
0.3513 0.2804 0.4206
0.3566 0.2856 0.4259
0.3619 0.2908 0.4312
0.3672 0.2960 0.4365
0.3725 0.3013 0.4417
0.3778 0.3065 0.4470
0.3831 0.3118 0.4522
0.3884 0.3171 0.4574
0.3937 0.3224 0.4626
0.3990 0.3277 0.4678
0.4042 0.3330 0.4729
0.3698
Eastern Region
Mean Min Max
0.5745 0.3491 0.9609
0.5787 0.3545 0.9615
0.5828 0.3598 0.9620
0.5870 0.3652 0.9626
0.5911 0.3705 0.9631
0.5952 0.3759 0.9636
0.5992 0.3812 0.9641
0.6033 0.3866 0.9646
0.6073 0.3918 0.9651
0.6113 0.3973 0.9656
0.6153 0.4026 0.9661
0.6193 0.4079 0.9666
0.6232 0.4132 0.9671
0.6271 0.4186 0.9675
0.6011
In order to better reflect the correctness of the
direction of public governance reform since the 18th
National Congress of the CPC, and further put
forward the effective improvement path, we can
analyze the factors causing the loss of public
governance technical efficiency as a reference. This
study analyzes the impact of three variables,
government size, urbanization rate and per capita
GDP, on technological loss, and the regression
results are shown in Table 4.
In terms of the natural conditions affecting the
technical efficiency of the output of public
governance, the estimated coefficient of government
scale is -0.0063, and is significant at the level of 1%,
indicating that the expansion of government scale is
conducive to the improvement of public governance
efficiency. However, from the point of view of the
value, its influence is not obvious, which can also
reflect that the scale of the government follows the
rationality of moderation and optimal. In terms of
the technical conditions affecting the technical
efficiency of public governance output, the
estimated coefficient of urbanization rate is -0.3177,
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
110

which is significant at the 1% level, indicating that
the improvement of urbanization rate is conducive to
improving the technical efficiency of public
governance. With the continuous development of the
economy and society and the continuous
improvement of the urbanization rate, the price of
the corresponding factors will continue to rise.
Based on the theory of "induced technological
change", the improvement of technological
productivity can replace some input factors of public
governance or enhance the accuracy of identifying
public service demands, thus helping to improve the
efficiency of public governance. In terms of regional
economic factors affecting the technical efficiency
of public governance output, the estimated
coefficient of per capita GDP is -23.8248, which is
significant at 1% level, indicating that the level of
economic development is positively correlated with
the technical efficiency of public governance.
Generally speaking, the higher the level of economic
development, the better the ability to improve
production technology, which also explains the
higher efficiency of public governance in the eastern
region. At the same time, the value of per capita
GDP estimation coefficient reflects the importance
of high-quality economic development to the
improvement of public governance efficiency, and
the two are mutually promoting relationship.
Table 4: Regression results of influencing factors of public
governance technology loss.
variable Coefficient
of
estimation
Standard
deviation
Z test
Size of
g
overnment
-
0.0063***
0.0012 -5.24
Rate of
urbanization
-
0.3177***
0.0095 -33.25
GDP per
capita
-
23.8248**
*
2.6214 -9.0
constant 0.8466*** 0.0059 142.60
Wald chi2
(3)
4579.89
0.0000
Prob≥
chibar2
Note: *, ** and *** are significant at the level of 10%, 5%
and 1% respectively.
3.2 Efficiency Decomposition of Public
Governance
According to the quadruple decomposition model of
total factor productivity, the efficiency of public
governance can be divided into four parts: the first
part and the second part are the technological change
and technological efficiency change of public
governance, and the third part reflects the change of
scale efficiency. If the scale efficiency is greater
than 0, it indicates that in the process of time change,
the increase of factor input caused by the change of
scale efficiency can promote the growth of public
governance efficiency. The fourth part is the change
of factor allocation efficiency, which reflects the
degree of deviation between factor elastic share and
factor cost share, and is an index to measure the
inefficiency of factor allocation. When the allocation
efficiency is less than 0, it indicates that the invalid
allocation of factors over time will inhibit the
growth of public governance efficiency. Considering
the lack of certain standards for the cost
measurement of factor input in the public
governance process, it is difficult to find a suitable
reference for the calculation of factor allot efficiency.
Therefore, this paper conducts decomposition and
empirical analysis on technology change ( ∆T ),
technology efficiency change ( ∆TE), total factor
productivity change ( ∆TFP) and scale efficiency
change (∆SE) in public governance efficiency, and
the results are shown in Table 5. With the passage of
time, the technical efficiency of public governance
increases gradually and becomes stable. The
potential cause of this phenomenon may be the low
efficiency of technology promotion. Although
technological innovation is active and new
technologies keep emerging, due to the lack of
resources and other factors, public governance
subjects cannot quickly adopt efficient new
technologies in a short period of time, and the
traditional governance concepts of many
governments also hinder the improvement of the
technical efficiency of public governance to some
extent. In addition, the scale efficiency of most
regions remains at a low negative level close to 0,
indicating that the increase of factor input caused by
the change of scale efficiency of public governance
may inhibit the growth of efficiency over time. This
also indicates that the current government-led
governance subject has not fully brought out the
enthusiasm of the reform of public governance and
cannot generate scale effect. Therefore, it is very
necessary to explore the concrete measures to
stimulate the circulation of factors.
Comparative Study on Statistical Measurement and Regional Differences of Chinese Public Governance Efficiency
111
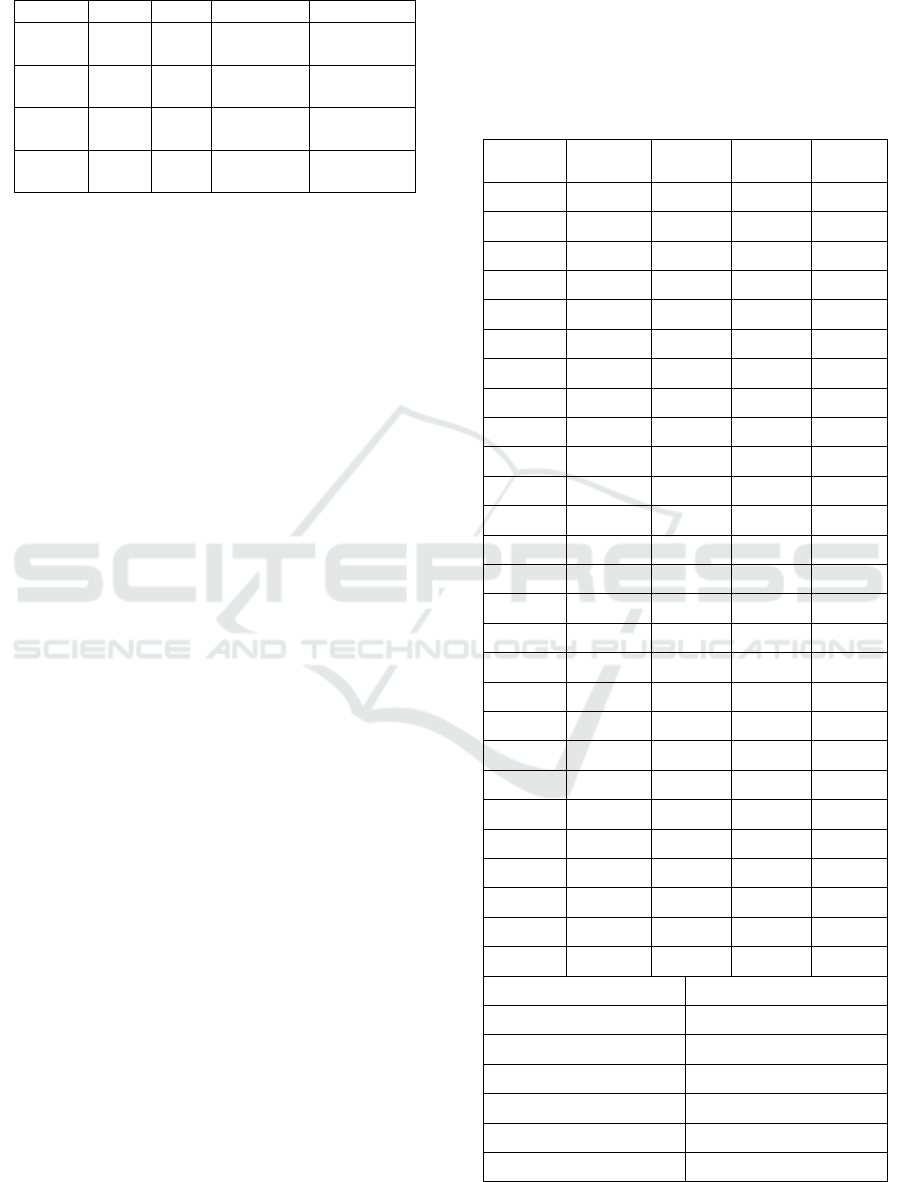
Table 5: Public governance efficiency growth and its
decomposition.
region
∆TFP ∆TE ∆T ∆SE
west 0.372
854
0.28
7173
0.076297 -0.021427
middle 0.449
635
0.24
8337
-0.048386 -0.000543
east 0.589
67
0.25
6643
-0.125129 -0.010624
Total 0.485
12
0.26
7500
-0.061863 -0.010404
4 CLASSIFICATION OF COUNTY
GOVERNMENT BASED ON
DECISION TREE C4.5
ALGORITHM
By 2020, China has 2,844 county-level
administrative regions, 2,084 of which have been
included in the China County Statistical Yearbook
2020. Due to the different conditions of resource
endowment and development of each county, the
research on the efficiency of public governance
cannot be generalized. By improving the traditional
regional division, counties in each province can be
further divided into several types according to the
three characteristics of regional area, population and
urbanization level, which is convenient to explain
the influence of relevant factors on the efficiency of
public governance. Therefore, based on the decision
tree C4.5 algorithm, the regional area, population
and urbanization level are divided into three
characteristics, namely large (large, high), medium
(general) and small (small, low), with a total of 27
types. The type with more than 15 cities is selected
for analysis.
The decision tree C4.5 algorithm uses the
gainratio and selects the most suitable attribute
according to the different attributes of the sample
training set to judge the sample type.
The greater the information entropy is, the
greater the disorder degree of data is. According to
the classification of maximum information gain, the
nodes of regional area, population and urbanization
level can be obtained as shown in Table 6. The
urbanization level is measured by (number of people
in the secondary industry + number of people
employed in the tertiary industry)/permanent
population. The step is to first divide the
urbanization level of 2,084 county-level
administrative regions to get the nodes of
urbanization level division, and then divide the
geographical area of 2,084 county-level
administrative regions. Based on the regional
division, the population is divided, as shown in
Table 6. A1-A27 is named according to the level of
urbanization, population and area.
Table 6: Decision tree classification of public governance
cities.
type
Numbr
of cities
Northea
st -1
East
Coast-2
North -
3
A1 7
A2 53 14
A3 78 40 5
A4 4 1
A5 29 8
A6 94 42 7
A7 13
A8 9 2
A9 49 15 10
A10 44 10 5 1
A11 121 5 27 2
A12 96 51 4
A13 21 5
A14 131 2 28 9
A15 155 2 41 44
A16 43 2
A17 97 5 14 14
A18 196 3 27 45
A19 50 12 1 1
A20 27 2 9
A21 10 1 1
A22 59 11 1
A23 87 11 9 3
A24 47 3 8
A25 82 7
A26 95 11 3 10
A27 92 2 8 30
West -4 Middle -5
3 4
8 31
2 31
3
8 13
12 33
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
112
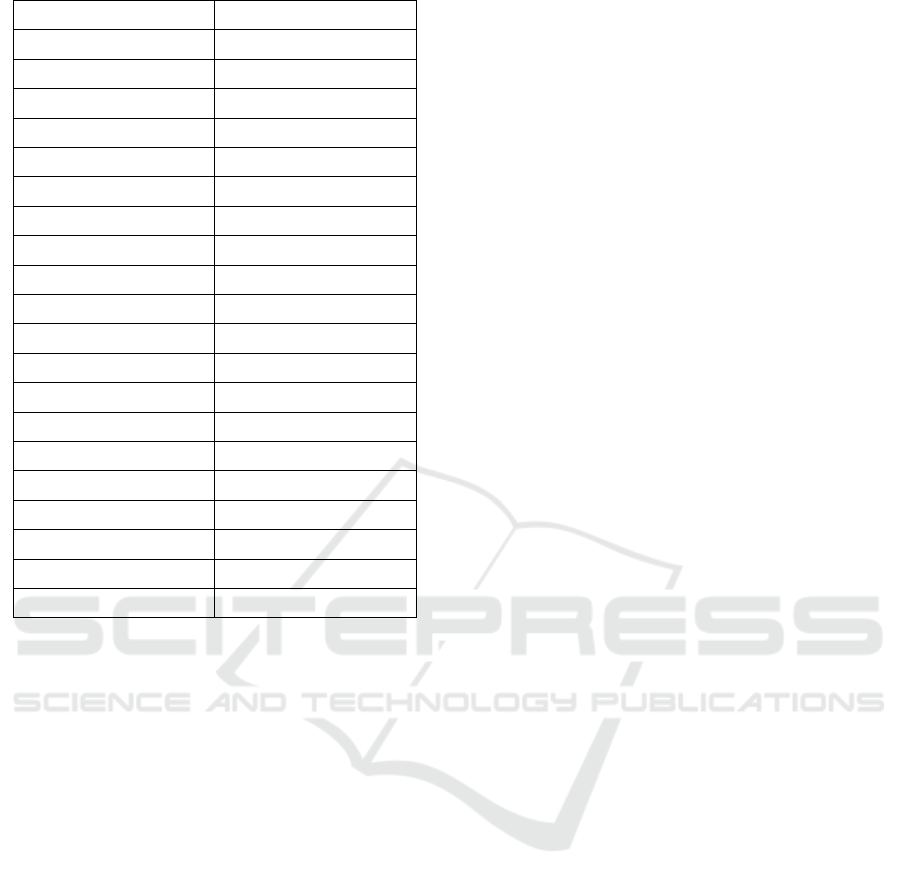
13
6 1
15 9
12 16
38 49
13 18
16
54 38
41 27
41
48 16
71 50
32 4
5 11
1 7
46 1
52 12
14 22
75
69 2
35 7
A1-A9 are counties with high urbanization level,
A10-A18 are counties with average urbanization
level, and A19-A27 are cities with low urbanization
level. It is not difficult to find that the level of
urbanization in Northeast China is in the second and
third grade, the eastern coastal cities are concentrated
in the first and second grade, the North and western
cities are concentrated in the second and third grade,
and the central cities are more average. According to
the results of model 6, urbanization rate and per
capita GDP have a significant negative impact on
efficiency loss. To some extent, it reflects that the
level of economic development will positively affect
the efficiency of public governance, which is also an
important reason for the regional development of the
efficiency of public governance. This also confirms
the spatial spillover of government governance
efficiency (He Baocheng et al.,2021). On the one
hand, regions with high governance efficiency will
bring "learning effect" and "demonstration effect",
driving the upgrading of surrounding industrial
structure, optimization of governance policies and
improvement of expenditure structure, thus
stimulating the positive spillover of efficiency. On
the other hand, regions with high efficiency have
relatively higher quality of economic development,
infrastructure, public services and market
environment, which will attract the inflow of factor
resources, resulting in the "siphon effect", leading to
the polarization clustering of high-end industries
such as knowledge and technology, thus exacerbating
the differences in government governance efficiency.
5 CONCLUSION
According to research and analysis, the efficiency of
public governance in China has increased steadily
since the 18th National Congress of the Communist
Party of China, with the highest in the eastern region,
which is related to the level of economic
development and the better optimization of
government scale. The efficiency of public
governance in the western region has been
significantly improved, which shows that with the
advancement of the modernization of national
governance, the western region has also experienced
new development. In the future, we should continue
to optimize the scale of the government and
constantly improve the rational flow of production
factors.
REFERENCES
Back, H. and Handenius, A., 2008, “Democracy and State
Capacity: Exploring a J- Shaped Relationship”, Govern
ance, Vol.21(1), pp.1~24.
BATTESE G E, COELLI T J. Frontier Production Functio
ns, Technical Efficiency and Panel Data: With Applicat
ion to Paddy Farmers in India[J]. Journal of Productivit
y Analysis,1992,3:I/2:153-169.
Guo Mengnan, Guo Jinhua. Governance Efficiency, Audit
management system reform and Total Factor Productiv
ity growth: Empirical evidence from 285 cities in Chin
a [J]. Modern finance and economics, 2021 (4) : 137-1
48. The DOI: 10.13676 / j.carol carroll nki cn36-1030 /
f 2021.04.013.
He Baocheng, Xiong Yongchao. How does National Audit
affect the efficiency of government governance? Analy
sis of spatial econometrics based on Tobit-SDM model
[J]. Audit & Economics Research,2021,36(06):16-25.
Wen Hong. Research on Public Administration under the G
overnance System: Review, Characteristics and Prospe
ct since the 18th National Congress of the Communist
Party of China -- Based on the Visual analysis of CSSC
I journal Papers [J]. Nanjing social science, 2018 (7): 5
6-64. The DOI: 10.15937 / j.carol carroll nki issn1001-
8263.2018.07.008.
Zhang Jiyuan. Study on Efficiency Evaluation of Public saf
ety Governance in Sichuan Province -- Based on DEA-
Tobit Model [J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong Univers
ity (Social Science Edition),20,21(03):63-70.
Comparative Study on Statistical Measurement and Regional Differences of Chinese Public Governance Efficiency
113
