
Efficiency Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis of Urban
Renewal Financial Expenditure in Liaoning Province
Yinghui Xiang, Yuhuan Meng and Zheng Liu
*
School of Management, Shenyang Jianzhu University, Shenyang 110168, China
Keywords: Urban Renewal, Financial Expenditure Efficiency, Influencing Factors, DEA-Tobit Model.
Abstract: In recent years, many provinces and cities in China have invested a large number of financial funds to support
urban renewal actions. Whether financial funds can be effectively used in urban renewal actions is related to
the implementation effect of urban renewal work. This paper uses DEA model to calculate the financial ex-
penditure efficiency of urban renewal in 14 cities of Liaoning Province, and further uses Tobit model to ana-
lyze the influencing factors of financial expenditure efficiency of urban renewal. The results show that Shen-
yang, Benxi, Liaoyang, Yingkou and Panjin have achieved DEA efficiency in the whole study period, and the
other cities still have relatively large room for improvement. Urban population density and urbanization rate
have a significant positive impact on the financial expenditure efficiency of urban renewal. Based on empirical
analysis, some suggestions are put forward to improve the financial expenditure efficiency of urban renewal.
1 INTRODUCTION
To solve the problem of urban development in the
stock age, urban renewal has become an important
strategy of urban development in the new period. In
2021, the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural De-
velopment and the People's Government of Liaoning
Province jointly issued the "Implementation Plan of
Urban Renewal Pilot Area jointly built by ministries
and provinces". The "Plan" proposes that by 2025, the
system and mechanism of jointly building urban re-
newal pilot areas by the ministries and provinces will
be initially established, and the vitality of the system
will be initially shown. In recent years, Liaoning
Province has made great achievements in urban re-
newal work, but it has also invested a large amount of
financial funds to promote urban renewal. Financial
support is crucial to urban renewal. Therefore, it has
an important practical significance to scientifically
evaluate the efficiency of financial expenditure in ur-
ban renewal in Liaoning Province and further explore
the influence of different factors on the efficiency of
financial expenditure.
At present, there are abundant achievements in the
research of urban renewal evaluation and analysis of
government expenditure efficiency at home and
abroad. With regard to the evaluation of urban re-
newal, Grace K.L. Lee and Edwin H.W. Chan (2008)
constructed an evaluation index system from the per-
spective of economic, social and environmental sus-
tainability, and applied AHP to evaluate the urban re-
newal in Hong Kong, China. Wang Meng et al.
(2011) took the former Xicheng District of Beijing as
an example, and used the DEA method of multi-ob-
jective decision-making to evaluate the comprehen-
sive performance of the old city reconstruction effect
in this area. Liu Guiwen et al. (2017) analyzed the
basic policy tools, categories and types of activities of
urban renewal in Shenzhen, constructed an evaluation
model of renewal policy to analyze the contradictions
and shortcomings of policy tools, and put forward rel-
evant suggestions for future policy formulation. Re-
garding the efficiency of government expenditure,
Balague-Coll et al. (2007) took the local government
of Valencia as an example, measured its government
efficiency by two-stage DEA method and unbounded
analysis method, and further used nonparametric
smoothing technology to analyze the influencing fac-
tors. Afonso et al. (2008) firstly used DEA method to
evaluate the financial expenditure efficiency of local
governments in Portugal, and then explained the effi-
ciency value through Tobit analysis, finding that in-
creasing education input and per capita purchasing
power is conducive to improving the efficiency of fis-
cal expenditure. Wang Qian et al. (2018) measured
the efficiency of local financial expenditure under the
restriction of public risk by SE-U-SBM-DEA model,
Xiang, Y., Meng, Y. and Liu, Z.
Efficiency Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis of Urban Renewal Financial Expenditure in Liaoning Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0012071000003624
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2022), pages 127-133
ISBN: 978-989-758-658-3
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
127

and analyzed its influencing factors by random effect
Tobit model.
In view of the shortcomings of the existing litera-
ture and learning from its experience, this paper in-
tends to use DEA-Tobit two-stage method to analyse
the financial expenditure efficiency and influencing
factors in urban renewal in Liaoning Province, with a
view to providing operational countermeasures and
suggestions for promoting the high-quality imple-
mentation of urban renewal in Liaoning and even the
whole country.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
2.1 Data Envelopment Analysis
Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) is a kind of non-
parametric testing method developed on the basis of
the concept of relative efficiency evaluation theory, It
was firstly put forward by Charnes, Cooper and
Rhodes in 1978. This method analyzes the input situ-
ation and output level data by selecting the decision
unit (DMU), and uses the linear planning method to
take the best input and output as the production fron-
tier, so as to form the data envelope curve. Among
them, the effective point has an efficiency value of 1
and lies on the front surface, while the ineffective
point will be given a relative efficiency value between
(0,1) and lies outside the front surface. According to
the variability of returns to scale, DEA model also in-
cludes CCR model with fixed returns to scale and
BCC model with variable returns to scale. For the
government, the input variable is more controllable
than the output variable. Therefore, after comprehen-
sive consideration, this paper will select BCC model
as the theoretical research model based on input ori-
entation. The model description is as follows,
=≤≥≥
=
=−
=+
−+
=
=
−
=
+
njss
sy
sy
ts
j
n
j
j
n
j
yjj
n
j
xjj
,...,2,1,0,0,0
1
..
min
1
1
1
0
0
λ
λ
θλ
θλ
θ
(1)
2.2 Panel Tobit Model
In order to deeply analyze the influencing factors and
degree of financial expenditure efficiency of urban re-
newal in Liaoning Province, according to the effi-
ciency value obtained by DEA model in the first
stage, the influencing factors are analyzed and evalu-
ated by panel Tobit model in the second stage. The
basic form of the model is as follows,
≤
++
=
00
0
0
i
iiii
i
Y
YX
Y
,
>,
εββ
(2)
In this paper, the financial expenditure efficiency
of urban renewal in Liaoning Province measured in
the first stage is taken as the dependent variable, and
the objective factors that may affect this efficiency
are selected as the independent variable to establish
the panel Tobit model, and the maximum likelihood
estimation (ML) method is used to estimate the vari-
able parameters.
3 THE EFFICIENCY
EVALUATION OF FINANCIAL
EXPENDITURE FOR URBAN
RENEWAL IN LIAONING
PROVINCE
3.1 Index Selection and Data Sources
The research object of this paper is the financial ex-
penditure efficiency of urban renewal in Liaoning
Province, so 14 cities in Liaoning Province are se-
lected as decision-making units. In view of the avail-
ability and completeness of data, 2016-2020 is se-
lected as the research interval. The relevant data
comes from the Statistical Yearbook of Liaoning
Province, the Financial Yearbook of China from 2017
to 2021 and the statistical database of China Eco-
nomic Net, and the evaluation index system of finan-
cial expenditure efficiency of urban renewal in Liao-
ning Province is constructed as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Evaluation Index System of Urban Renewal Financial Expenditure Efficiency in Liaoning Province.
Tar
g
et Invest Out
p
ut
Index
Expenditure on shantytown renovation Regional GDP per capita
Expenditure on urban construction Urban financial revenue
Expenditure on technology research and
develo
p
ment
Per capita residential floor area
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
128
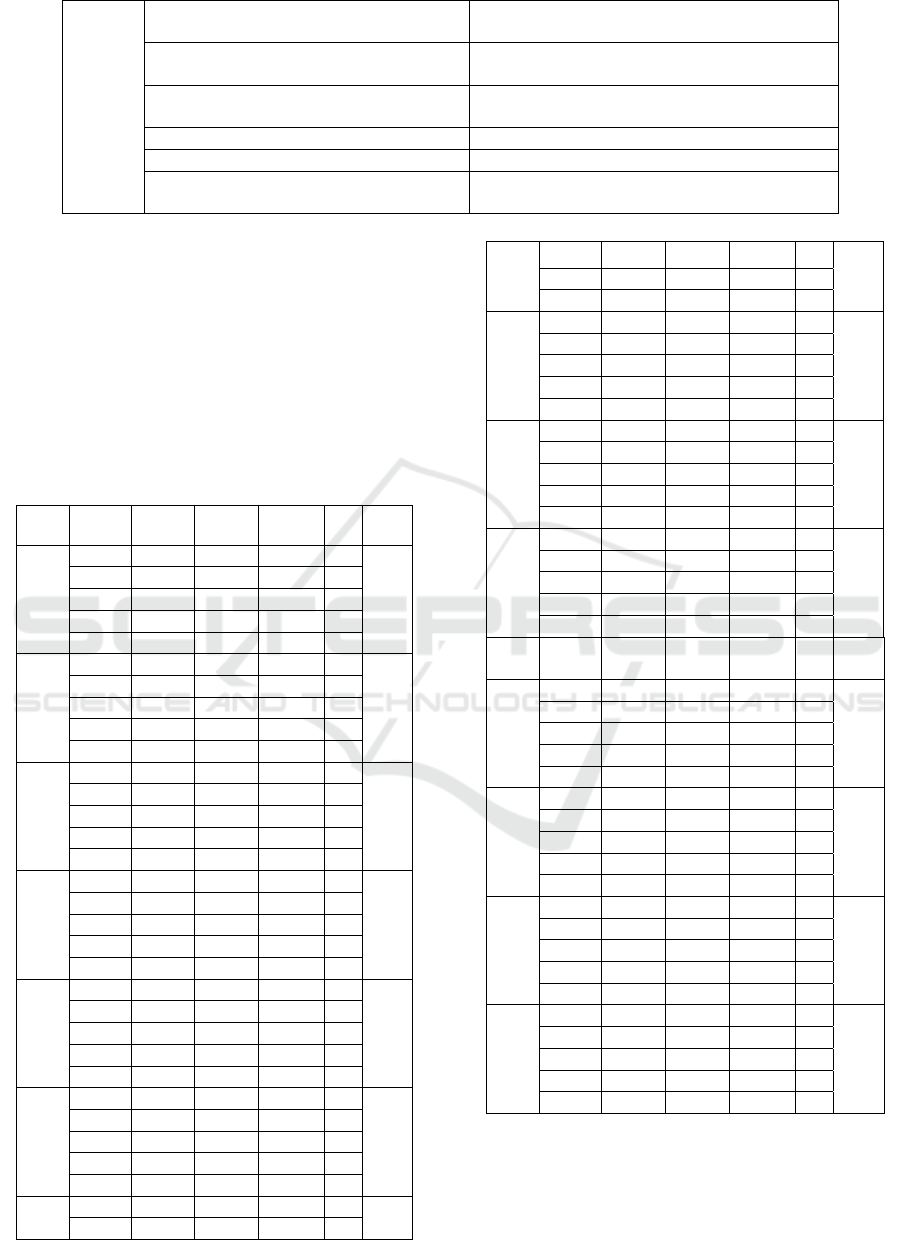
Expenditure on pollution prevention and
control
Per capita urban road area
Expenditure on community public facili-
ties in urban and rural areas
Park green area per capita
Expenditure on affordable housing pro-
j
ects
Heating area
/
Length of urban drainage pipeline
/
Daily treatment capacity of urban sewage
/
Harmless treatment capacity of domestic gar-
b
a
g
e
3.2 Analysis of Empirical Results
This paper selects the VRS input-dominant model of
DEA model, uses DEAP2.1 software to calculate the
financial expenditure efficiency of urban renewal in
14 cities in Liaoning Province from 2016 to 2020, the
calculation results are analyzed at the overall and re-
gional levels in Liaoning Province.
Table 2: Scores of Urban Renewal Financial Expenditure
Efficiency.
CIT
Y
TIME
CRST
E
VRST
E
SCAL
E
RA
NK
She
nya
ng
2016 1 1 1 -
1
2017 1 1 1 -
2018 1 1 1 -
2019 1 1 1 -
2020 1 1 1 -
Da-
lian
2016 0.965 1 0.965
drs
3
2017 0.947 1 0.947
drs
2018 0.954 1 0.954
drs
2019 0.986 1 0.986
drs
2020 1 1 1 -
An-
sha
n
2016 0.907 0.908 0.999
irs
4
2017 0.994 0.997 0.997
drs
2018 1 1 1 -
2019 0.99 1 0.99
drs
2020 0.949 1 0.949
drs
Fu-
shu
n
2016 1 1 1 -
2
2017 0.946 0.946 1 -
2018 0.946 0.949 0.997
drs
2019 1 1 1 -
2020 1 1 1 -
Ben
xi
2016 1 1 1 -
1
2017 1 1 1 -
2018 1 1 1 -
2019 1 1 1 -
2020 1 1 1 -
Dan
don
g
2016 0.758 0.759 0.999
drs
8
2017 0.804 one 0.804
drs
2018 0.789 0.834 0.946
drs
2019 0.859 0.907 0.947
drs
2020 0.789 0.795 0.993
irs
2016 0.828 0.97 0.854
drs
9
2017 0.724 0.746 0.97
drs
Jin-
zho
u
2018 0.71 0.727 0.977
drs
2019 0.593 0.622 0.953
drs
2020 0.766 0.77 0.995
irs
Yin
gko
u
2016 1 1 1 -
1
2017 1 1 1 -
2018 1 1 1 -
2019 1 1 1 -
2020 1 1 1 -
Fu
xin
2016 1 1 1 -
5
2017 0.939 0.972 0.965
irs
2018 0.915 0.962 0.951
irs
2019 0.926 0.972 0.953
irs
2020 0.888 0.963 0.922
irs
Lia
oya
ng
2016 1 1 1 -
1
2017 1 1 1 -
2018 1 1 1 -
2019 1 1 1 -
2020 1 1 1 -
CIT
Y
TIM
E
CRS
TE
VRS
TE
SCA
LE
RA
N
K
Pan-
jin
2016 1 1 1
-
1
2017 1 1 1
-
2018 1 1 1
-
2019 1 1 1
-
2020 1 1 1
-
Tieli
ng
2016 0.732 0.747 0.98
irs
6
2017 0.733 0.788 0.931
irs
2018 1 1 1
-
2019 0.846 0.858 0.986
irs
2020 0.81 0.838 0.967
irs
Cha
oyan
g
2016 0.704 0.732 0.962
irs
10
2017 0.734 0.753 0.975
drs
2018 0.738 0.741 0.997
drs
2019 0.723 0.86 0.841
drs
2020 0.701 0.813 0.863
drs
Hul
udao
2016 0.91 1 0.91
drs
7
2017 0.946 0.946 1 -
2018 0.946 0.949 0.997
drs
2019 1 1 1 -
2020 1 1 1 -
3.2.1 Overall Analysis
According to the results calculated by DEA, the trend
chart of average values of three efficiency scores of
14 cities in Liaoning Province from 2016 to 2020 was
Efficiency Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis of Urban Renewal Financial Expenditure in Liaoning Province
129
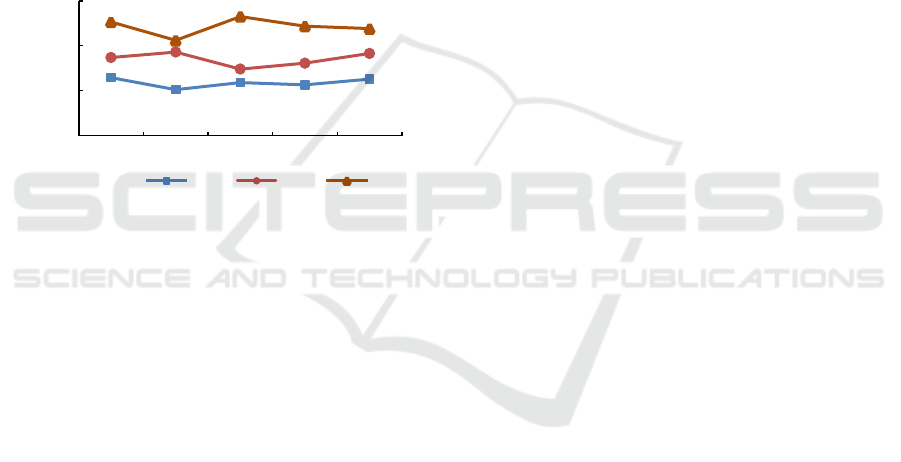
drawn, as shown in Figure 1. As can be seen from
Figure 1, the overall efficiency of financial expendi-
ture for urban renewal in Liaoning Province de-
creased first and then increased, with little fluctua-
tion, and the efficiency values were all above 0.9; the
trend of scale efficiency is similar to the overall com-
prehensive efficiency, and the technical efficiency
curve is below the scale efficiency curve in the whole
stage, which indicates that the low technical effi-
ciency is the main reason why the financial expendi-
ture efficiency of urban renewal in Liaoning Province
cannot be greatly improved, and the key to improving
the efficiency lies in improving the backward tech-
nology of financial capital utilization. Therefore, the
government should pay more attention to the tech-
nical innovation and management efficiency of urban
renewal expenditure funds, and lay emphasis on im-
proving the use level of urban renewal related funds.
Figure 1: Trends of the overall urban renewal financial ex-
penditure efficiency.
3.2.2 Regional Level Analysis
From the perspective of comprehensive efficiency,
the cities with effective comprehensive efficiency in
the whole stage include Shenyang, Benxi, Liaoyang,
Yingkou and Panjin (comprehensive efficiency value
is 1), followed by Fushun, and Chaoyang has the low-
est comprehensive efficiency, with an average value
of only 0.720, By consulting and analyzing the origi-
nal data, it is found that there is obvious input redun-
dancy and diminishing returns to scale in this city.
From the perspective of technical efficiency, Shen-
yang, Dalian, Benxi, Liaoyang, Yingkou and Panjin
have reached the effective level (the technical effi-
ciency value is 1), and Jinzhou has the lowest tech-
nical efficiency, with an average value of only 0.767,
which is relatively backward. From the perspective of
scale efficiency, Shenyang, Benxi, Liaoyang, Ying-
kou and Panjin have reached an effective level (the
scale efficiency value is 1), which shows that the
scale and structure of urban renewal financial ex-
penditure in these cities are gradually becoming rea-
sonable, while the rest of the regions have not reached
the optimal efficiency level, and the scale of financial
expenditure needs to be adjusted. From the perspec-
tive of returns to scale, except Shenyang, Benxi, Liao-
yang, Yingkou and Panjin, the financial input of ur-
ban renewal in other cities generally deviated from
the optimal scale during the whole inspection period,
and most cities suffered from diminishing returns to
scale, while Fuxin and Tieling were in an increasing
state in most years. From the analysis of Table 2, it
can be seen that there is no direct relationship be-
tween the financial expenditure efficiency of urban
renewal and the degree of economic development,
and the high-efficiency output may not come from
high input, which may be due to the different eco-
nomic development modes and financial expenditure
structures in different places. Blindly expanding in-
vestment is not a wise move. It is necessary for local
governments to optimize and adjust the supply struc-
ture and improve the investment mode according to
the urban development.
4 ANALYSIS OF INFLUENCING
FACTORS OF FINANCIAL
EXPENDITURE EFFICIENCY
OF URBAN RENEWAL IN
LIAONING PROVINCE
4.1 Selection of Influencing Factors
At present, there are few research results about the in-
fluencing factors of financial expenditure efficiency
in urban renewal, but there are many in-depth re-
search results. Therefore, based on a large number of
literatures, this paper summarizes various influencing
factors that are often selected in the existing results.
Combined with the attributes and development char-
acteristics of urban renewal, and taking into account
the availability of data, this paper selects five factors:
regional economic development level, urban popula-
tion density, urbanization rate, urban renewal finan-
cial investment scale and education level of residents
to examine their impact on urban renewal financial
expenditure efficiency.
0,850
0,900
0,950
1,000
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
MEAN
TIME
CRSTE VRSTE SCALE
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
130
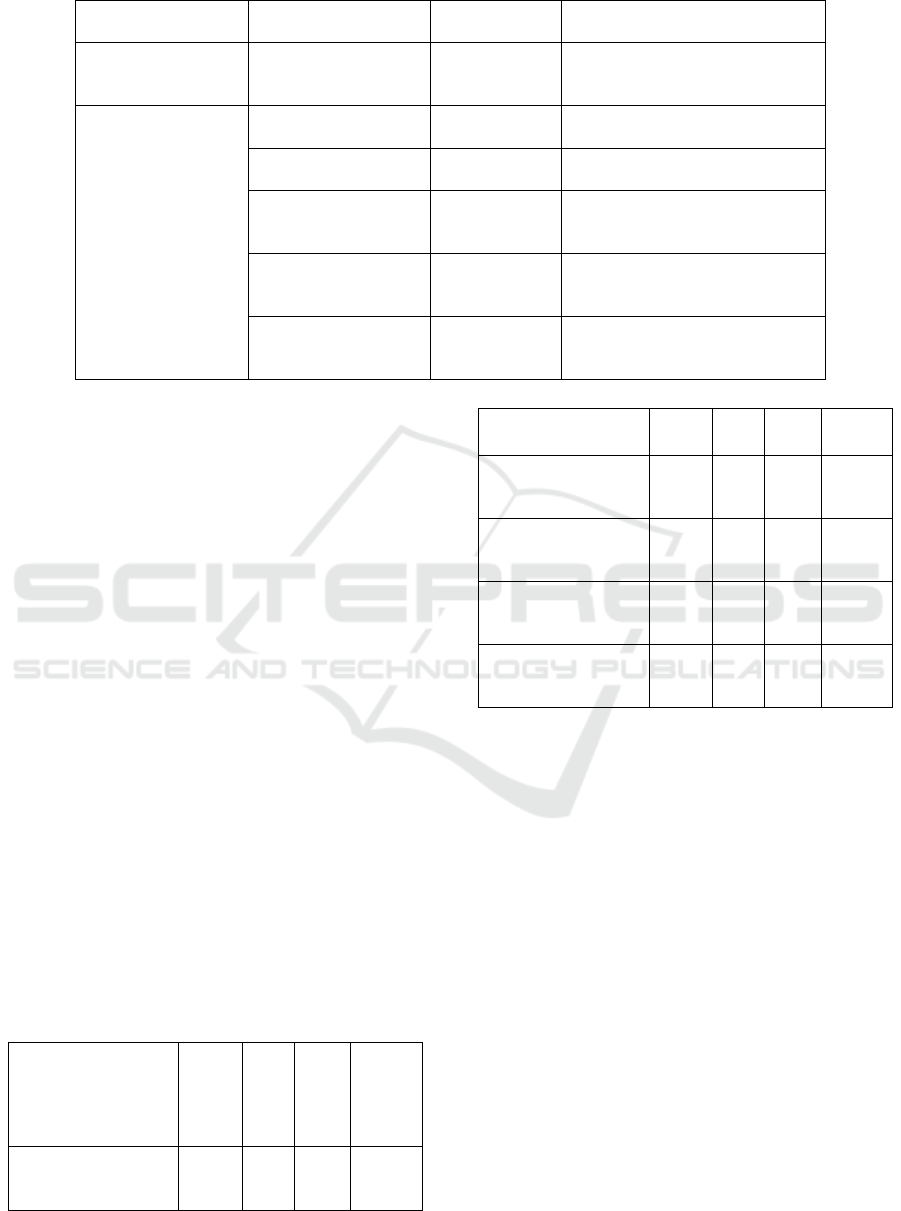
Table 3: Description of influencing factors variables.
Statistical variable Variable name
Variable Sym-
b
ol
Variable Explanation
Dependent Variable
Financial expenditure
efficiency in urban
renewal
eff Comprehensive efficiency value
Independent Varia-
ble
Regional economic
develo
p
ment level
gdp Urban per capita GDP
Urban population
densit
y
pd
Total urban population/Regional
area
Urbanization rate urban
Number of permanent urban resi-
dents/Total permanent popula-
tion of the re
g
ion
Urban renewal finan-
cial investment scale
scale
Financial expenditure on urban
renewal/Total expenditure of city
finance
Education level of
residents
edu
Number of students enrolled in
various schools/Total regional
p
opulation
4.2 Establishment of Tobit Regression
Model
Based on the calculation of the financial expenditure
efficiency of urban renewal in Liaoning Province
from 2016 to 2020 by using the DEA-BCC model, the
Tobit model is constructed to further explore the fac-
tors affecting the financial expenditure efficiency of
urban renewal. In order to smooth the data, the re-
gional economic development level(gdp) and urban
population density(pd) are logized to improve the sta-
tionarity of explanatory variables. The Tobit model in
this paper is set as follows,
itiitit
itititit
eduscale
urbanpdgdpeff
εμββ
β
β
β
β
++++
+++=
54
3210
)ln()ln(
(3)
4.3 Analysis of Tobit Regression
Results
Eviews10.0 software is used to make regression anal-
ysis on the influencing factors of financial expendi-
ture efficiency of urban renewal in Liaoning Prov-
ince. The Tobit regression results are summarized in
Table 4.
Table 4: Tobit regression results of influencing factors.
Influencing Factor Coef
Std.
Err
Z
Sig-
nifi-
cant
Level
(P>Z)
Regional economic
development level
-
0.069
443
0.0
497
95
-
1.39
0.1631
455
7
Urban population
density
0.072
085*
*
0.0
358
36
2.01
151
0.0443
Urbanization rate
0.007
834*
**
0.0
014
76
5.30
631
0
Urban renewal fi-
nancial investment
scale
0.022
026
0.0
227
37
0.96
874
6
0.3327
Education level of
residents
0.035
552
0.0
240
21
1.48
005
9
0.1389
Note: * * *, * * and * are significant at the levels of 1%, 5%
and 10% respectively.
The regression coefficient of regional economic
development level (gdp) to urban renewal financial
expenditure efficiency is negative, indicating that
there is a negative relationship between them, but it is
not significant, which means that regional economic
development level will not have a significant impact
on urban renewal fiscal expenditure efficiency. It may
be because some areas with higher level of economic
development pay more attention to the urban environ-
ment, which can promote the implementation of ur-
ban renewal. However, there are also some areas that
unilaterally pursue economic benefits, ignoring the
necessary transformation actions for urban adverse
environmental areas, to some extent, it weakens the
efficiency of urban renewal financial expenditure.
The regression coefficient of urban population
density (pd) to urban renewal financial expenditure
efficiency is significantly positive, which indicates
that the increase of urban population density can im-
prove agglomeration economic benefits and financial
Efficiency Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis of Urban Renewal Financial Expenditure in Liaoning Province
131

expenditure efficiency. The reason may be that the
higher the population density, the higher the public's
requirements for living conditions, which is condu-
cive to improving the efficiency of urban renewal fi-
nancial expenditure.
The regression coefficient of urbanization rate
(urban) to the efficiency of urban renewal financial
expenditure is significantly positive, which indicates
that the increase of urbanization rate can obviously
improve the efficiency of urban renewal financial ex-
penditure. On the one hand, the improvement of ur-
banization level means that a large number of rural
people gather in cities, resulting in scale effect,on the
other hand, with the gradual improvement of urban
spatial layout and functional structure, the relative en-
vironment of urban financial input and output be-
comes better, which is more conducive to the rational
allocation of urban financial resources by the govern-
ment and the promotion of urban financial expendi-
ture efficiency.
The regression coefficient of urban renewal finan-
cial investment scale (scale) to urban renewal finan-
cial expenditure efficiency is positive, indicating that
there is a positive relationship between them, but it is
not significant. It may be because the funds invested
in some areas have not been effectively allocated, and
there are unreasonable or wasteful phenomena, which
leads to low efficiency of financial expenditure.
Therefore, local governments should determine the
scale of financial investment in urban renewal accord-
ing to local conditions.
The regression coefficient of education level of
residents (edu) to the efficiency of urban renewal fi-
nancial expenditure is positive, indicating that there
is a positive relationship between them, but it is not
significant. Generally speaking, the higher the educa-
tion level of residents, the higher their support and en-
thusiasm for urban renewal, and they can play a better
role under the local reasonable public participation
mechanism of urban renewal. However, some urban
public participation mechanisms are imperfect, the
implementation effect is not in place, and they fail to
play an effective role, thus restricting the efficiency
of urban renewal financial expenditure to some ex-
tent.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
According to the results of empirical analysis in this
paper, and by comparing the average calculation re-
sults of comprehensive efficiency, technical effi-
ciency and scale efficiency of cities in Liaoning prov-
ince during the whole research period, it can be seen
that there are significant differences among different
cities, and Shenyang, Benxi, Liaoyang, Yingkou and
Panjin are DEA efficient, meanwhile, they are both
technically efficient and scale efficient. The scale ef-
ficiency values of Dalian, Fuxin and Huludao are
lower than the technical efficiency values, which in-
dicates that the scale efficiency leads to the low level
of comprehensive efficiency in these cities, and the
investment scale should be adjusted reasonably. An-
shan, Fushun, Dandong, Jinzhou, Tieling and Chao-
yang have low comprehensive efficiency because the
technical efficiency is lower than the scale efficiency.
Therefore, should be made to adjust and improve the
government management structure or level. Through
further analysis of influencing factors, it is found that
urban population density and urbanization rate play a
significant role in promoting urban renewal, There is
a positive but not significant relationship between ur-
ban renewal financial investment scale and education
level of residents, while there is an insignificant neg-
ative relationship between regional economic devel-
opment level and urban renewal financial expenditure
efficiency. In view of this, this paper puts forward the
following countermeasures and suggestions:
Optimize the structure of government financial
expenditure and determine the scale of urban renewal
financial expenditure according to local conditions.
Give full play to the role of human capital and en-
courage the development of innovative and high-tech
enterprises.
Accelerate the formation of regional economic
layout with complementary advantages and high-
quality development, and promote the high-quality
development of cities.
REFERENCES
Afonso C, Fernandes E. Assessing and explaining the rel-
ative efficiency of local government [J]. The Journal of
Socio-Economics, 2008, 27(5).
CHARNES A,COOPER W W,RHODES E. Measuring
the efficiency of decision making units [J]. European
Journal of Operational Research, 1978, 2(6): 429-
444.
Liaoning Provincial People's Government. "Implementa-
tion Plan of Urban Renewal Pilot Area Jointly Built by
the Ministry and the Province" .2021-08-02.
Lee G K L, Chan E H W. The Analytic Hierarchy Process
(AHP) Approach for Assessment of Urban Renewal
Proposals. Social Indicators Research.2008.89(1).
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
132

Liu Guiwen, Zhiyong Yi, Wei Lizhen, Hu Xinyu. Research
on urban renewal policy based on the perspective of
policy tools: taking Shenzhen as an example [J]. Urban
Development Research, 2017,24 (03): 47-53.
Maria Teresa Balaguer-Coll, Diego Prior, Emili Tortosa-
Ausina. On the determinants of local government per-
formance: A two-stage nonparametric approach[J].
European Economic Review, 2007, 51(2): 425-451.
Wang Qian, Dong Yanling. Evaluation of the efficiency of
local fiscal expenditure in China under the constraint of
public risk and analysis of influencing factors [J]. Fi-
nancial Research, 2018, (11): 46-61+70.
Wei Quanling. Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA)[M].
Beijing: Science Press, 2015.
Wang Meng, Li Yan, Zhang Wenxin, He Cenhui. Perfor-
mance evaluation of urban renewal based on DEA
method-taking the former Xicheng District of Beijing
as an example [J]. Urban Development Research, 2011
(10): 90-96.
Efficiency Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis of Urban Renewal Financial Expenditure in Liaoning Province
133
