
Does Local Debt Governance Ease Corporate Financing Constraints?
Empirical Evidence from Chinese A-share Listed Companies
Banchi Xia
Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China
Keywords: Local Debt Governance, Financing Constraints, Listed Companies, Difference-In-Difference.
Abstract: Local debt governance is an important practice of China's economy in the new era. Based on the A-share data
of Chinese listed companies from 2010 to 2019, this paper takes the 2015 "New Budget Law" as an exogenous
impact and constructs an intensity DID model. The research finds that local debt governance will make
companies reduce cash on hand, thereby effectively alleviating the impact of corporate debt. A series of
robustness tests prove the rationality and effectiveness of the DID model. The results of heterogeneity analysis
show that local debt governance has different effects on alleviating the financing constraints of different types
of enterprises. Among them, the effect on non-state-owned enterprises is stronger than that on state-owned
enterprises, and the effect on high-tech enterprises is stronger than that on low-tech enterprises. What’s more,
the role of enterprises is stronger for enterprises in inland cities than for enterprises in coastal cities. This
paper provides relevant policy suggestions for optimizing local debt governance and promoting the high-
quality development of enterprises in the new era.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist
Party of China, the central government has issued a
series of policies to administer local debts, the
fundamental purpose of which is to prevent and
resolve financial risks. Local government debt
governance is an important fiscal and financial
system reform of the Chinese government since the
new era, and it has played an important role in the
financial sector, micro-market entities, and monetary
and credit sectors. During the 2008 financial crisis,
the Chinese government introduced a large-scale
stimulus plan to expand domestic demand, drive
investment, and ease the pressure of the financial
crisis. Local governments have chosen to issue local
bonds on a large scale in order to collaborate with the
central government's policies, and most of the debts
have not been included in the budget management.
There have been problems such as large debts,
insufficient supervision, and unclear responsibilities.
In response to these problems, the Chinese
government issued the “Budget Law of the People's
Republic of China in 2014” to coordinate and guide
the governance of local debt. It has also continuously
amended the law, standardized the governance
methods and introduced them to all localities, solved
problems left over from history, enhanced the
supervision of local debt, and fully included local debt
in the tabled budget.
Enterprise financing constraints make enterprises
confront problems such as high financing costs,
difficult financing, and slow financing speed. These
problems have a particularly obvious impact on small
and medium-sized enterprises. The increase in the cost
of the financing process will cause the company to
abandon a part of the original investment activities
with a positive net present value when investing and
has to choose an investment with higher net income
and greater risk, changing the existing investment
structure of the company, and facing Higher risk
management costs. Enterprise financing constraints
hinder the long-term healthy development of
enterprises, which may cause some enterprises to
withdraw from the market due to cost reasons, reduce
market competition, affect market vitality, and thus
deal a blow to the country's overall economy. Easing
corporate financing constraints helps companies
obtain sufficient cash flow to support their rapid
development, prompts companies to optimize their
investment structure, diversify their investments to
diversify their investment risks, and promote the long-
term sustainable development of the capital market.
308
Xia, B.
Does Local Debt Governance Ease Corporate Financing Constraints? Empirical Evidence from Chinese A-Share Listed Companies.
DOI: 10.5220/0012074200003624
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2022), pages 308-316
ISBN: 978-989-758-658-3
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

To explore the impact of local debt governance on
corporate financing constraints is of significant
significance to China's capital market, which is
conducive to standardizing the development of
marketization and stimulating the investment and
financing activities of enterprises. The innovation
points and contributions of this paper are as follows:
First, in terms of content, the implementation of the
New Budget Law in 2015 is taken as a quasi-natural
experiment, and the investment and financing
activities of enterprises are included into the
governance framework system of local government
debt, which is conducive to revealing the influence of
local debt governance on micro subjects. Secondly,
the intensity DID model was used to accurately
identify the causal effect and solve the possible
endogeneity and missing variable bias. This paper
provides experience references for the virtuous circle
of government debt and the high-quality development
of micro market players in the new era.
The remaining contents of this paper are arranged
as follows: the second part is the policy background
and literature review, the third part is the data
processing and model setting, the fourth part is the
baseline regression and robustness test, the fifth part
is the heterogeneity analysis, and the sixth part is the
conclusion and policy enlightenment.
2 BACKGROUND AND
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 System Background
Since China's reform and opening up policy, with the
establishment of the market economic system, the
scale of local government debt has been expanding.
The government is making efforts to make the
issuance of local bonds more transparent and
institutionalized through supervision. With the
historical change of the concept of social and
economic development in the new era, the debt
governance mode needs to be changed from the
traditional quantitative governance based on GDP to
the performance governance oriented by long-term
benefits, and focus on improving the quality and
efficiency of debt financing.
Since China entered the fast lane of economic
development in the 1990s, the speed of urbanization
has accelerated, and more and more attention has
been paid to the construction of infrastructure in
various regions to protect people's livelihoods and
further promote economic development. In this
situation, the local government is facing huge
pressure from a shortage of funds and stagnant
development. In order to ease the economic pressure
on local governments, China began to implement the
local debt policy to raise funds for local governments
to support their development. The issuance of local
government bonds in China can be divided into four
stages. The first stage is from 2009 to 2010, China
implemented the policy of issuing and repaying on
behalf of the central government. The Ministry of
Finance should issue the "2009 Local Government
Bond Budget Management Measures", which
formulated the policy of the Ministry of Finance to
issue local bonds on behalf of local governments. In
the same year, the State Council approved the
Ministry of Finance to issue 200 billion yuan of local
bonds as an agent. The second stage is from 2011 to
2013, China implemented the pilot project of self-
issued local debt repayment by local governments.
The Ministry of Finance issued the "Pilot Measures
for Issuing Bonds by Local Governments in 2011",
which designated Shanghai, Guangdong, Zhejiang,
and Shenzhen as pilot areas for voluntary repayment,
and the policy of repayment and repayment is still
implemented in other regions except for the pilot
area. The third stage is from 2014 to 2015, China
implemented the pilot project of local government
self-issue and self-repayment of local debt. The
"2014 Local Government Bond Self-Issuance and
Self-Repayment Pilot Measures" issued by the
Ministry of Finance stipulated that local governments
have the right to voluntarily issue book-keeping fixed
bonds. Interest rate bonds. In the same year, the "New
Budget Law" was revised and would be officially
implemented from 2015. Article 35 of it stipulates
that part of the funds for construction investment
necessary for the budgets of provinces, autonomous
regions, and municipalities approved by the State
Council may be borrowed through the issuance of
local government bonds within the limit determined
by the State Council, furthermore standardize the
policies related to the self-issue and self-repayment
of local debt. The fourth stage is from 2015 to the
present, the issuance of the "Local Government
General/Special Bond Budget Management Method"
marks the full implementation of local governments'
self-issued and self-repaid local debts. The issuance
of local government bonds in China presents the
characteristics that the issuer goes from top to bottom
and the scale of issuance gradually increases.
At present, China's local government debt model
has formed an institutional framework with notice,
measures, and opinions as the main body, with the
Ministry of Finance as the core regulatory body, the
Does Local Debt Governance Ease Corporate Financing Constraints? Empirical Evidence from Chinese A-Share Listed Companies
309

People's Bank of China, the China Banking
Regulatory Commission and the National
Development and Reform Commission as the central
point, and other departments as the response points.
In the "management measures", the focus is on the
policy design of borrowing, using, and repayment.
2.2 Literature Review
The existing literature on research on local debt and
micro-market entities is carried out from two aspects,
one of which is the impact of local debt on the
economy, and the other is the relationship between
local debt and corporate financing.
2.2.1 Local Debt and Economy System
With the gradual acceleration of regional
construction in China, local governments are facing
increasing financial pressure. In order to meet the
financial needs of local governments, the scale of
local bond issuance has also increased rapidly. Large
local debts and long debt repayment time have also
led to problems such as insufficient government
repayment capacity, unsound risk management and
control mechanisms, and debt invisibility (Zhou &
Ren 2020). Local governments in China are also
carrying out local debt management while
implementing the local debt policy. The methods and
key points of local debt governance have always been
hotly debated issues in academic circles. (Tao 2015)
pointed out that the government needs to improve the
fiscal transparency of local governments and reform
the fiscal system. (Guo & Mao 2019) believe that the
debt governance model needs to shift from traditional
quantitative governance based on gross domestic
product to long-term benefit-oriented performance
governance, focusing on improving the quality and
efficiency of debt financing. (Li, Zhou, Liu & Ge
2022) believe that local governments need to promote
debt legislation, formulate a sound public debt law,
and establish a social monitoring mechanism for the
use of debt funds. However, the conclusions of the
academic circles are not uniform regarding the impact
of local debt governance on Chinese economic
development. (Zhang & Wang 2009) pointed out that
only by strictly controlling the risks of local bond
issuance can local bonds promote the development of
China's economy, while (Zheng & Zhang 2020)
believed that the growth of local bonds may inhibit
technological innovation, enterprises, and
investment, thereby inhibiting the development of the
real economy. (Tang 2022) pointed out that the scale
of local government debt in China has exceeded a
reasonable threshold, and the crowding out effect of
debt expansion on the real economy is more obvious.
(Panizza & Presbitero 2013) pointed out that the
relationship between government debt and economic
growth is not monotonous, and the threshold of
monotonic transition may not be single. (Wu 2014)
also confirmed through empirical evidence that there
is a nonlinear relationship between economic growth
and local government debt.
2.2.2 Local Debt and Corporate Financing
Constraints
The impact of local debt on corporate behavior is
multifaceted. (Yang & Song 2015) believed that local
debt can not only have a micro impact on corporate
behavior but may also lead to macro risks such as
fiscal risks and financial risks, thereby affecting
corporate behavior. The direct impact of local debt on
enterprises is reflected in the impact on corporate
innovation. High R&D companies are more likely to
be exposed to government debt than low R&D
companies (Croce, Nguyen, Raymond & Schmid
2019). (Xu, Li, Feng, Wu, & He 2021) studied the
data of China's Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share listed
companies and 31 provinces' local debts and
concluded that local debts have a relatively strong
crowing-out effect on corporate R&D investment.
(Zhang, Yin & Wang 2021) conducted an empirical
study to show that the level of hidden debt in local
government debt has a significant inhibitory effect on
the patent applications of local companies and leads
to a reduction in internal R&D expenses. Some
scholars conduct research on state-owned enterprises
and private enterprises separately. (Liang, Shi, Wang
& Xu 2017) found that the expansion of local
government debt greatly crowded out the leverage of
non-state-owned enterprises, and also crowded out
the leverage of state-owned enterprises. (Huang,
Pagano & Panizza 2020) found that local debt
restricts the investment of private enterprises by
tightening capital restrictions, but does not affect the
investment of state-owned enterprises.
Existing literature has different views on whether
local debt can effectively alleviate corporate financing
constraints. (Luo & Mi 2010) believed that local debt
is an effective way to solve the current financing
difficulties of SMEs. It enables small and medium-
sized enterprises to get rid of the discrimination of
banks and other financial institutions in indirect
financing. (Demirci, Huang & Sialm 2019) studied the
data of several countries and found that there is a
negative correlation between government debt and
corporate leverage, and government debt crowds out
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
310

corporate debt. However, (Zhen, Zhang, She, Shen &
Chen 2020) used the PVAR model to carry out
empirical analysis and concluded that the growth of
local debt and financial efficiency are two-way
linkages and mutual promotion; while the growth of
local debt will crowd out financing for private SMEs
and push up financing costs.
3 METHODS AND MATERIALS
3.1 Experimental Subject
The empirical analysis in this paper uses three major
databases: the first is the A-share database of Chinese
listed companies from 2010 to 2019, which includes
the basic information of listed companies, total assets,
total liabilities, owners' equity, cash flow and other
financial indicators, as well as the patent information
of enterprises. The second is the 2010-2019
prefecture-level city database, which includes
population, GDP, primary industry, secondary
industry, tertiary industry and other relevant
information at the prefecture-level city level. The
third is the local debt database for 2010-2019, which
contains the total outstanding debt of prefecture-level
cities and can measure the scale and timing of debt
issuance. The data used in this demonstration are all
from the CSMAR database.
3.2 Empirical Method
3.2.1 Methodology
Since this empirical study is about the change of
corporate financing constraints before and after the
implementation of China's local debt governance
policies, we choose the DID model to evaluate the
policy effect. Compared with other statistical
methods, the DID model can control the qualitative
heterogeneity that does not change over time, avoid
the endogeneity problem, alleviate the missing
variable bias problem, and better reflect the changes
of the research object before and after a certain
exogenous impact.
3.2.2 Model Setting
In order to identify the causal effect of the "New
Budget Law" implemented in 2015, we constructed an
intensity DID model. Because the "New Budget Law"
in 2015 was rolled out at a comprehensive level at
once without a pilot, therefore, ordinary DID cannot
be used for estimation, we use the intensity of local
debt issuance in the database to group according to the
median, among which those greater than or equal to
the median enter the treatment group, and those less
than the median enter the control group. Taking this
as the core, the model is constructed as follows:
cflow
=α
+α
treat ∗ post +α
X
+δ
+σ
+φ
+ε
(1)
Among them, 𝑐𝑓𝑙𝑜𝑤
represents the financing
constraints of i enterprises in city c in year t, 𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑡
represents the grouping according to the intensity of
local debt issuance, 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑡 is a policy dummy
variable, 𝛿
represents a dummy variable at the
enterprise level, 𝜎
represents a dummy variable at
the city level, and 𝜎
represents a dummy variable at
the time level, 𝜀
representing the random
disturbance term.
The statistical analysis software used in this paper
is Stata17. Table 1 shows the code interpretation of
the explanatory variables and the explained variables
used in Stata. Figure 1 is a statistical description of
the variables studied in this paper.
Table 1: Code interpretation of the statistical variables.
Var ia ble c od e Var ia ble
cash Cash holdings
did
𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑡 ∗ 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑡
size Company size; ln (TA)
lnSale Logarithm of the operating income
lnage Logarithm of the age of a listed company
roa ROA
roe ROE
rjgdp Urban GDP per capita
decyzb The added value of the secondary industry accounted for GDP
dscyzb The added value of the tertiary industry accounted for GDP
rkzrzzl Natural population growth rate
fisspt Financial freedom
fiscal Scale of fiscal expenditure
Does Local Debt Governance Ease Corporate Financing Constraints? Empirical Evidence from Chinese A-Share Listed Companies
311
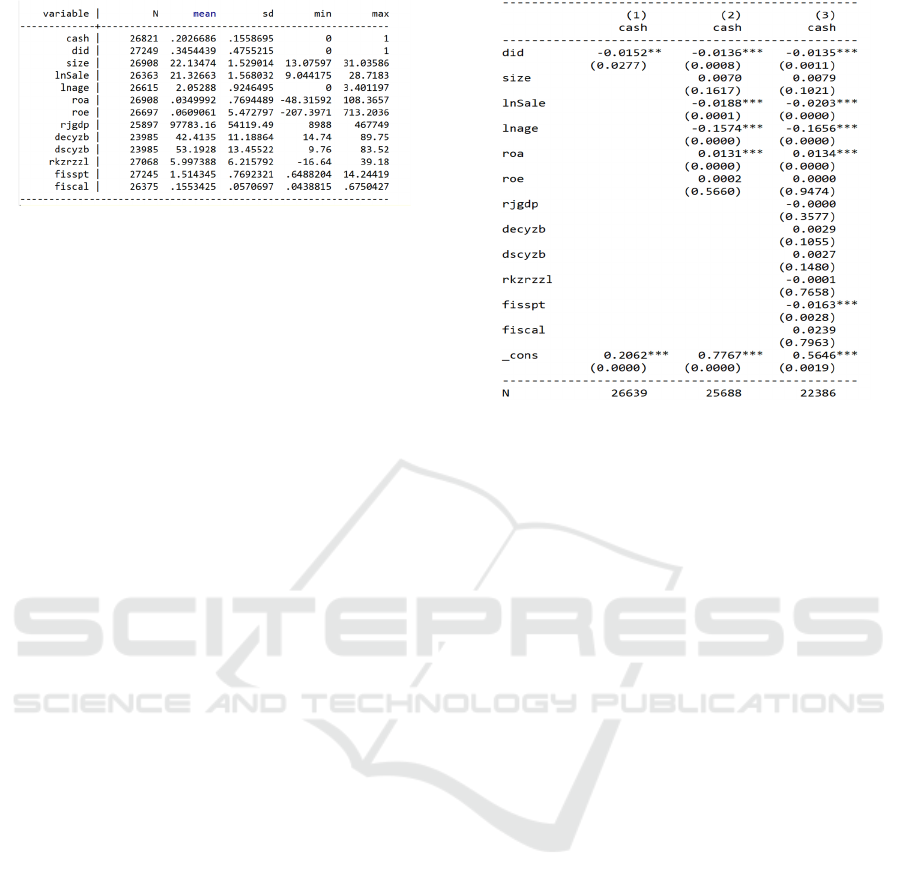
Figure 1: Statistical description of variables.
4 BASIC REGRESSION AND
ROBUSTNESS TEST
4.1 Basic Regression
We use the database of listed companies to verify the
benchmark regression model. The regression results
are shown in Figure 2. Column (1) is the company’s
cash on hand as the explained variable. We can find
that the regression result is negative and significant at
5%. Column (2) added the control variables at the
enterprise level on the basis of column (1), we can see
that the direction of the regression result is still
unchanged, and the significance is 1%; then, we add
the control variables at the city level variable, the
regression results are shown in column (3) in Figure
2, we can find that the result is still significantly
negative at the 1% level. It can be found that after the
implementation of the new budget law, local
governments have strengthened the management of
debt quotas, financing constraints in the entire market
have been relaxed, more resources will flow into
enterprises, and enterprises’ expectations for the
future will become better. Under normal
circumstances, the company will increase investment
and reduce cash on hand, so we found that the cash
on hand of the company has decreased through
regression, and the financing constraints have been
eased at this time.
Figure 2: Basic regression results.
4.2 Robustness Test
4.2.1 Parallel Trend Test
We use the event study method to test the parallel
trend, on this basis, construct the econometric model
as follows:
cflow
=α
+βtreat∗
D
+α
X
+δ
+σ
+φ
+ε
(2)
Among them, D
is an event-time dummy
variable with a value of 0 or 1. The value of k
ranges from −3 to 3. When k0, the value is 1 in
the k-th year before the policy shock occurs,
otherwise it is 0; when k0, the value is 1 in the k-
th year after the policy shock occurs, otherwise it is
0; if k=0, the value is 1 in the year when the policy
shock occurs, otherwise it is 0. When doing
regression, we will use it as a baseline group to
compare the difference between the treatment group
and the control group.
Figure 3 shows the test results of parallel trends.
The dot in the figure represents the estimated value of
did coefficient, reflecting the financing constraints of
the enterprise. The dotted line passing through the dot
and perpendicular to the horizontal axis represents the
95% horizontal confidence interval. pre3-pre2
represents the estimated value of did coefficient
corresponding to the three years before the
occurrence of the policy to the two years before the
occurrence of the policy. post1-post3 represents the
estimated value of did coefficient corresponding to
one year to three years after the occurrence of the
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
312
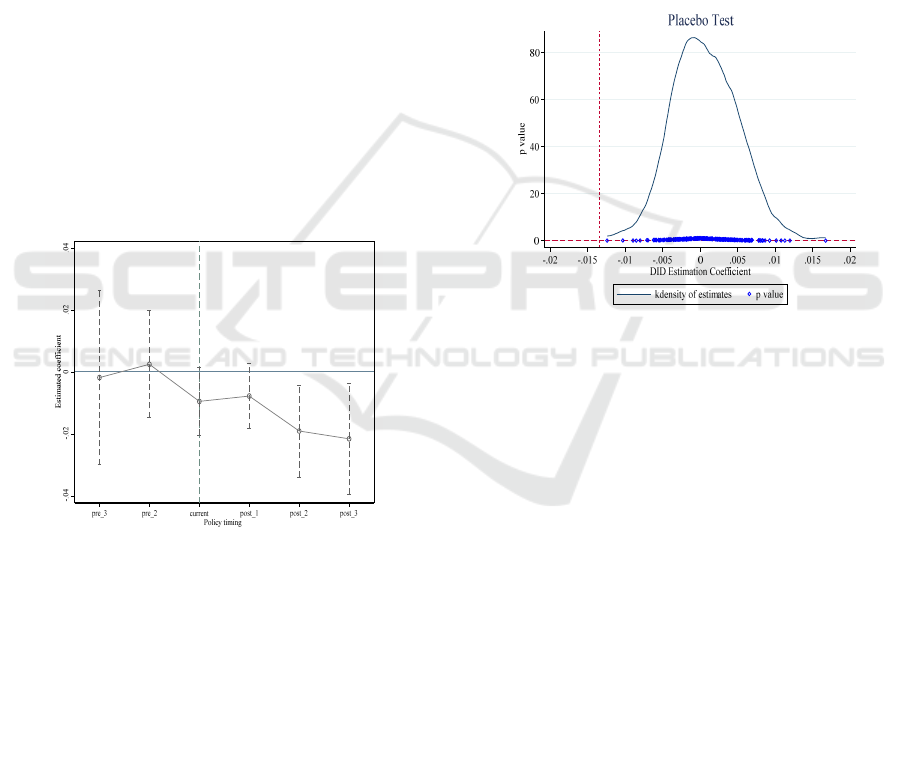
policy. As shown in the figure, pre3-post1 fluctuates
around 0, which corresponds to a wider 95%
confidence interval and crosses 0, indicating that
there is no significant difference between the
treatment group and the control group compared with
the year before the implementation of the New
Budget Law in 2015. In summary, before the policy
impact occurred, the gap between the enterprises in
the treatment group and the control group in
financing constraints did not change significantly,
indicating that the parallel trend hypothesis was valid.
In addition, Figure 1 also reflects the dynamic impact
of policy shocks on corporate financing constraints.
post2-post3 is significantly negative, which proves
that local debt governance policies only take effect
two years after their implementation, and corporate
cash inventory decreases, reflecting that corporate
financing constraints have been alleviated to some
extent. From the perspective of the size of the
regression coefficient, the coefficient of local debt
governance has a downward trend since the second
year after the implementation of local debt
governance policy, which proves that the easing
effect of local debt governance on corporate
financing constraints has gradually increased.
Figure 3: Parallel trend test.
4.2.2 Placebo Test
Select all enterprises in the year of policy
implementation in 2015 from the overall panel data,
randomly select 50% of the enterprises and match
them with the overall panel data, 50% of the
enterprises selected are used as the experimental
group, and the rest are used as the control group. Do
DID processing on it, and repeat this process 200
times. The final result is shown in Figure 4, which
shows the results of 200 random processes, where the
X-axis represents the size of the estimated coefficient
of the "pseudo-policy dummy variable", the Y-axis
represents the density value and p value, and the
curve is the estimated coefficient Kernel density
distribution, the dots are the p-values corresponding
to the estimated coefficients, the vertical dotted line
is the true estimated value of the DID model −0.013,
and the horizontal dotted line is the significance level
of 0.1. It can be seen that most of the estimated
coefficients are concentrated around zero, and most
of the p-statistics are greater than 0.1. The real
estimated value of the DID model is an obvious
outlier, indicating that the policy implementation
effect is significantly different from the placebo
effect, and the reform of the new budget law on local
debt is the reason for the change in corporate
financing constraints.
Figure 4: Placebo test.
5 HETEROGENEITY ANALYSIS
5.1 State-Owned Enterprises and Non-
State-Owned Enterprises
The nature of the enterprise is an important reason
that affects the financing constraints of the enterprise.
According to the attribution of enterprise ownership,
we divide the enterprises studied into state-owned
enterprises and non-state-owned enterprises, and
include them in the regression respectively, as shown
in Figure 5, in which columns (1) and (2) is the
regression result of non-state-owned enterprises, and
columns (3) and (4) are the regression results of state-
owned enterprises. We can see from the regression
results that the regression results of columns (1) and
(2) are negative and significant at the 1% level, and
the regression results of columns (3) and (4) are also
Negative, but only significant at the 10% level. The
results prove that local debt governance has a greater
impact on non-state-owned enterprises. State-owned
Does Local Debt Governance Ease Corporate Financing Constraints? Empirical Evidence from Chinese A-Share Listed Companies
313
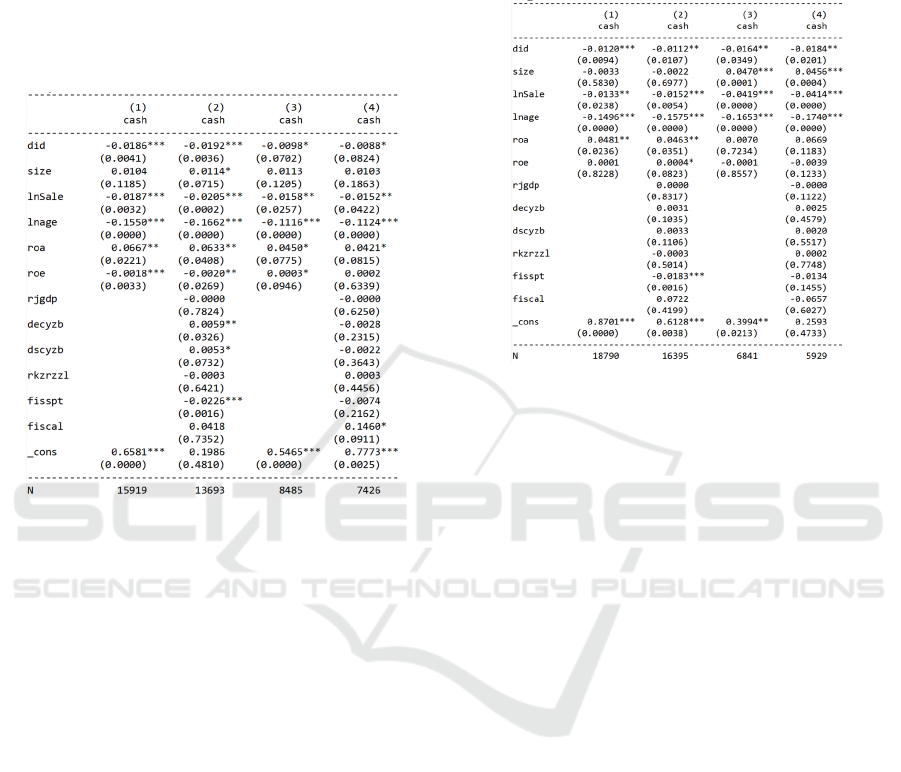
enterprises funded by the state have sufficient and
stable financing and lower financing costs. Compared
with state-owned enterprises, non-state-owned
enterprises have more financing needs and face
financing difficulties. Under the situation of local
debt control, resources will be further tilted to non-
state-owned enterprises. At this time, the financing
constraints of non-state-owned enterprises will be
greatly eased.
Figure 5: Heterogeneity analysis of state-owned enterprises
and non-state-owned enterprises.
5.2 High-Tech Industries and
Low-Tech Industries
The industry in which the enterprise is located also
has an important impact on the financing constraints
of the enterprise. From this perspective, we divide
enterprises into high-tech industry enterprises and
low-tech industry enterprises, and include them in the
regression respectively, as shown in Figure 6, where
columns (1) and (2) are the regression results of
enterprises in non-high-tech industries, and columns
(3) and (4) are the regression results of enterprises in
high-tech industries. The regression results show that
after adding all the control variables, the regression
results of columns (2) and (4) are both negative and
significant at the 5% level, but we can see that the
regression of high-tech enterprises The coefficient is
significantly higher than that of enterprises in low-
tech industries, indicating that local debt governance
is more effective in alleviating financing constraints
in high-tech industries. Generally speaking,
enterprises in the high-tech industry need to invest
more in R&D and innovation, so they need more
capital investment to obtain patents. Therefore, the
financing needs of enterprises in the high-tech
industry are more vigorous. Resources will flow to
high-tech industry enterprises, thereby easing their
financing constraints and helping their sustainable
development.
Figure 6: Heterogeneity analysis of high-tech industries and
low-tech industries.
5.3 Coastal and Inland Areas
The regional location of the enterprise will also have
a certain impact on the financing constraints of the
enterprise. According to the location of the enterprise,
we divide the enterprise into coastal area enterprises
and inland area enterprises and include them in the
regression, as shown in Figure 7. Columns (1) and (2)
are inland enterprises, columns (3) and (4) are coastal
enterprises. We can find from the regression results
that the regression results of columns (1) and (2) are
negative and significant at the 1% level, but the
regression results of columns (3) and (4) are not
significant. This indicates that local debt governance
can ease financing constraints in inland areas much
more than that in coastal areas. This difference is
mainly caused by two reasons. One is that the
government’s local debt and its governance model in
coastal areas are more open and transparent than
those in inland areas, and the financing process of
enterprises is more standardized; Compared with
enterprises in inland areas, enterprises in coastal areas
have more abundant financing channels, and
enterprises in coastal areas also have the advantage of
easier access to overseas financing funds. The
financing channels of enterprises in inland areas are
mainly bank loans or corporate debt financing. After
the government fully implements the local debt
management policy, the effect of expanding
financing channels for enterprises in inland cities is
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
314

more obvious than that for enterprises in coastal
cities.
Figure 7: Heterogeneity analysis of coastal areas and inland
areas.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND POLICY
IMPLICATIONS
Based on the A-share data of Chinese listed
companies from 2010 to 2019, this paper takes the
2015 "New Budget Law" as an exogenous shock,
constructs an intensity DID model, and studies the
causal effect of local debt governance on corporate
financing constraints. The results of the basic
regression show that local government debt
governance will make enterprises reduce cash on
hand, thus achieving the effect of effectively
alleviating corporate financing constraints. Parallel
trend test and placebo test proved the rationality and
validity of the DID model. The results of
heterogeneity analysis show that local debt
governance has different effects on alleviating the
financing constraints of different types of enterprises.
Among them, the effect on non-state-owned
enterprises is stronger than that on state-owned
enterprises, and the effect on high-tech enterprises is
stronger than that on low-tech enterprises. The role of
enterprises is stronger for enterprises in inland cities
than for enterprises in coastal cities.
Based on the above research conclusions, this
paper proposes the following policy implications.
First, local debt governance can effectively alleviate
the financing constraints of enterprises. Local
governments should take this opportunity to further
complete open and transparent governance based on
the existing policy framework of local debt issuance,
reasonably control the scale of local debt issuance,
improve the local debt governance system, reduce the
"crowding out effect" on enterprises, and thus
promote local construction. Second, strengthen the
relevant supervision of local debt issuance. The
central government needs to assume the external
supervision task of local government debt issuance,
and the local government also needs to optimize the
policy of local debt issuance, so that local debt can
really play its role and promote the development of
China's macro and micro economy. Third, local
government should further optimize and improve the
capital market, reduce the financing costs of
enterprises, effectively solve the dilemma of
"difficult and expensive financing" for enterprises,
stimulate the economic vitality of market players, and
promote the high-quality development of enterprises.
REFERENCES
Croce, M. M., Nguyen, T. T., Raymond, S., Schmid, L.
(2019). Government debt and the returns to innovation.
J. Financ. Econ. 132, 205–225.
Demirci, I., Huang, J., Sialm, C. (2019). Government debt
and corporate leverage: International evidence. J.
Finan. Econ. 133, 337–356.
Guo, Y., Mao, J. (2019). Local Government Debt
Governance in China in the Past 70 Years: Review and
Prospect. China Finan. Econ. Rev. 8, 49–65.
Huang, Y., Pagano, M. & Panizza, U. (2020). Local
Crowding‐Out in China. J. Finan. 75, 2855–2898.
Luo, S., Mi, M. (2010). Local bonds and small and
medium-sized enterprise financing preliminary
exploration. J. Hangzhou Teach. College (Soc. Sci. Ed.)
(06), 114–119.
Li, X., Zhou, Y., Liu, S., Ge, X. (2022). The characteristics
of local government debt governance: evidence from
qualitative and social network analysis of Chinese
policy texts. Econ. Res. 35, 6037–6066.
Liang, Y., Shi, K., Wang, L., Xu J. (2017). Local
government debt and firm leverage: evidence from
china: local government debt and firm leverage. Asian
Econ. Policy Rev. 12, 210–232.
Panizza, U., Presbitero, A.F. (2013). Public debt and
economic growth in advanced economies: A survey.
Swiss J. Econ. Stat. 149, 175–204.
Tao, K. (2015). Assessing Local Government Debt Risks in
China: A Case Study of Local Government Financial
Vehicles. China World Econ. 23, 1–25.
Tang, Z. (2022). Local Government Debt, Financial Circle,
and Sustainable Economic Development.
Sustainability. 14, 11967.
Wu, Y. (2014). Local government debt and economic
growth in china. BOFIT Discussion Papers.
Does Local Debt Governance Ease Corporate Financing Constraints? Empirical Evidence from Chinese A-Share Listed Companies
315

Xu J., Li Y., Feng, D., Wu, Z., He Y. (2021). Crowding in
or crowding out? how local government debt influences
corporate innovation for china. PLoS ONE 16,
e0259452.
Yang, H., Song C. (2015). Local government debt, property
rights and corporate tax burden. Collected Essays
Finan. Econ. 197, 27–36.
Zhou, L., Ren, J. (2020). Analysis of the causes and
countermeasures of local government debt problems in
China. J. Hunan Finan. Econ. Univ. 36, 94–101.
Zhang, Y., Wang, Z. (2009). On the economic growth
guaranteed by local government debt. Chin. Foreign
Entrep. (10), 111–112.
Zhang, L., Yin, Z., Wang, S. (2021). Local Government
Implicit Debt and Corporate R&D Activities: Evidence
from Chinese Non-financial Listed Companies. J.
Finan. Econ. 47, 94–107.
Zhen, X., Zhang, Q., She, Y., Shen, R., Chen, S. (2020).
Research on the dynamic relationship between local
government debt, financial efficiency and financing of
private SMEs—Empirical analysis of PVAR model
based on inter-provincial panel data. Finan. Account.
Int. Commer. (04), 78–86.
Zheng, X., Zhang, Q. (2020). Discussion on the influence
mechanism of local government debt growth on the
development of real economy: --The intermediary
effect model analysis based on inter-provincial panel
data. New Econ. (07), 81–92.
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
316
