
Development of STEM Based e-Module Using Flip PDF Corporate on
Energy Conservation Law Materials
Dwi Sulistyaningsih, Rifa’atul Maulidah and IfaRifatul Mahmudah
Physics Education, Siliwangi University, Siliwangi Street No. 24, Tasikmalaya 46115, Indonesia
Keywords: Conservation of Energy, e-Module, STEM.
Abstract: This study aims to develop a STEM-based e-module on energy conservation law. This research uses the
Research and Development (R&D) method with a 4D development model. The 4D development model
consists of four main stages: define, design, develop, and disseminate. The evaluation of validators comprised
of media and material experts carried out this research to the build stage. The Data collection techniques are
through interviews; the student needs analysis and validation questionnaires from media and content experts.
The results showed that the percentage of product value based on media experts was 94.91%, with valid
criteria covering aspects of appearance, presentation, and quality of supporting media. The product value
based on material experts is 95.00%, with valid criteria, including parts of the suitability of practicum
objectives with learning outcomes, clarity of practicum series, and STEM components. Thus, the STEM-
based e-module on the energy conservation law material has met the valid criteria for teaching materials in
practical activities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Education is the most crucial aspect of the
development of a country because education aims to
prepare quality human resources to face challenges in
the 4.0 industrial revolution era(Syahirah et al.,
2020). Education that is held must be able to improve
the quality of one's self in order to be able to adapt to
advances in the field of technology which is
increasing rapidly(Sari, 2020). The creation of
intelligent, responsible and adaptive human beings to
the development of the times can be realized through
education, in particular through science learning.
Science learning aims for individuals to have mastery
of the basics of science followed by mathematical
abilities. Mastery of the basics of science and
mathematics can be obtained through learning using
the STEMapproach(Zulaiha & Kusuma, 2020).
STEM is an approach that integrates science,
technology, engineering and mathematics in the
learning process. The application of technology is a
supporting tool to help students understand the
concepts being studied. The application of the
technique aims to train students to design, assemble,
draw, and do other activities so that students
understand the procedures for solving problems.
Furthermore, mathematics aims to simplify the
concept of science itself more systematically and
mathematically(E. Susanti et al., 2021). Applying
STEM to learning can encourage students to design,
develop and utilize technology and apply
knowledge(A. Susanti, 2020).
Accuracy in choosing the presentation method or
approach is the key to success in actualizing the
learning outcomes that have been formulated(A.
Susanti, 2020). In addition to the choice of approach,
the quality of learning and the achievement of
learning objectives are also influenced by the use of
teaching materials(Arisya et al., 2021). One of the
teaching materials that educators can develop is a
module. A module is a teaching material that is
systematically arranged in a language that is easily
understood by students according to their level of
knowledge and age so that they can learn on their own
(independently) with minimal assistance or guidance
from educators(Prastowo, 2012). Technological
advances have developed the print module into an
electronic module (e-module). E-module is an
embodiment of multimedia-based teaching materials.
E-modules were born due to teaching materials
integrated with technological advances(Pratiwi,
2021). E-modules can be developed on a STEM basis.
STEM-based e-modules are electronic learning
46
Sulistyaningsih, D., Maulidah, R. and Mahmudah, I.
Development of STEM Based e-Module Using Flip PDF Corporate on Energy Conservation Law Materials.
DOI: 10.5220/0012196400003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 46-51
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

modules that integrate related disciplines. The use of
STEM-based modules in learning can build
professional characters who have skills, good time
management, work with colleagues, use technology
and effective ways to solve a problem being discussed
(Syahirah et al., 2020).
The law of conservation of energy in this study
describes the conservation of mechanical energy. The
law of conservation of mechanical energy explains
that an object's total mechanical and potential energy
at any point is always constant. The magnitude of the
mechanical energy at any point is sometimes constant
due to the influence of non-conservative forces acting
on objects(Sulistyaningsih et al., 2022). The amount
of mechanical energy that is not constant due to non-
conservative forces is a discussion that needs further
study by students in learning. Proof of the law of
conservation of energy can be done by using a mini
roller coaster.
The mini roller coaster is a prototype designed to
resemble the trajectory of a roller coaster
ride(Maulidah et al., 2022). This tool has been
successfully designed in the fundamental physics
laboratory, but the module for using this tool in
learning fundamental physics has yet to be available.
Therefore, the researchers took the initiative to
develop a STEM-based e-module on energy
conservation law. In developing the e-module,
researchers will use the software flip PDF corporate.
This software is easy to use, with the appearance of
publishing as a flip (back and forth) like an actual
book.
2 METHOD
This study uses the Research & Development (R&D)
method. In this study, the crucial target is developing
STEM-based e-modules on energy conservation law
materials to be used in fundamental physics courses.
This study used a 4D model consisting of four main
stages: define, design, develop and disseminate. This
research is limited only to the development stage. The
activities carried out at each stage of development are
described as follows.
2.1 Define
The define stage is a stage that aims to determine and
define the needs in the development process. This
stage is often called a needs analysis. In the context
of developing teaching materials in the form of e-
modules, the definition stage is carried out by:
2.1.1 Curriculum Analysis
Curriculum analysis is carried out by reviewing the
curriculum documents used by the study program so
that the curriculum needs develop teaching materials.
2.1.2 Formulate Learning Objectives
Learning objectives need to be formulated to limit the
extent to which teaching materials will be developed.
2.1.3 Analysis of Student Needs
Analysis of students' needs for teaching materials in
the form of e-modules needs to be done to determine
whether development needs to be carried out based on
the needs of students. Student needs are analyzed by
distributing questionnaires to students who have
contracted fundamental physics courses.
2.2 Design
The design stage aims to produce a prototype that will
be made. The activity carried out at the design stage
is to outline the e-module that will be developed.
2.3 Develop
The Develop stage is the development stage of the
outline made at the design stage. After the product has
been successfully created, it is then evaluated by a
media and material expert validator. Validation is
done by giving a questionnaire to the validator to
assess the product developed according to the Likert
scale, which consists of four categories, namely:
Strongly Agree (SA), Agree (A), Disagree (D), and
Strongly Disagree (SD). In addition to providing an
assessment, validators are also asked to provide
suggestions to produce even better products. The
assessment results from the validator are then
presented using equation (1).
()
%100% ×
=
m
x
x
P
(1
)
With:
P
= average value (in%)
x
= total score
m
x
= maximum score
The calculation results are then interpreted based on
the table of product validity criteria presented in
Table 1.
Development of STEM Based e-Module Using Flip PDF Corporate on Energy Conservation Law Materials
47
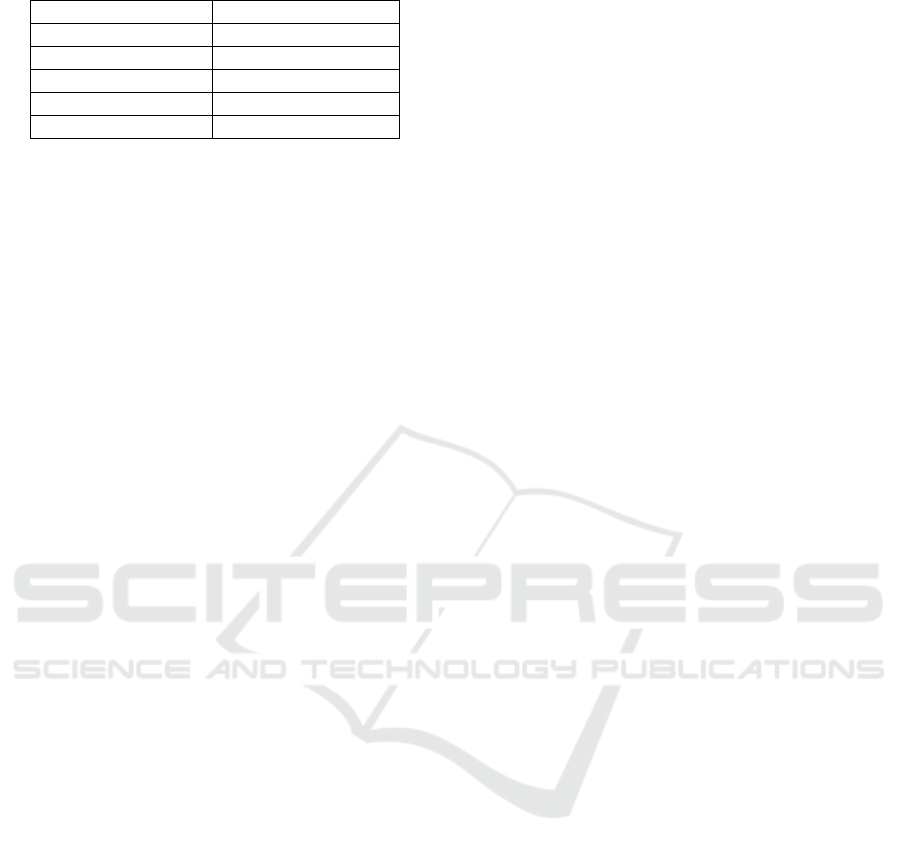
Table 1: Product Validity Criteria.
Percentage (%) Category
81 – 100 Very high
61 – 80 High
41 – 60 Moderate
21 – 40 Low
0 – 20 Very low
(Riduwan, 2010)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The product of this research is a STEM-based
practicum e-module on the law of energy
conservation. In developing this e-module, the steps
taken by the researcher are as follows.
3.1 Define
In the define stage, the researcher performs several
activities to determine and define the needs in the
development process. These activities are curriculum
analysis, formulating learning objectives, and
analyzing students' needs for practicum e-modules.
The analysis results are used as a reference in the
development of STEM-based e-modules on the law
of energy conservation.
3.1.1 Curriculum Analysis
In the curriculum analysis stage, the researcher
reviewed the curriculum document in the form of the
Syllabus for the Basic Physics I course used in the
Department of Physics Education, FKIP, Siliwangi
University. As a form of confirmation regarding the
contents of thedocument, the researcher also
conducted interviews with the lecturers in charge of
the courses. The results of the selected Sub-CPMK
curriculum analysis are Sub-CPMK-5; namely,
students can comprehensively identify the concept
and application of business and energy. Students are
expected not only to understand concepts but also to
be able to use the concepts learned to solve problems
related to everyday life. Support is needed in the form
of hands-on and contextual learning methods.
3.1.2 Formulate Learning Objectives
The learning objectives to be achieved through
practicum activities using STEM-based e-modules on
the law of energy conservation consist of goals from
knowledge and skills aspects. From the aspect of
knowledge, the learning objectives to be achieved are
that students can apply the concept of work and
energy to solve problems related to energy
conservation law on mini roller coasters. From the
skill aspect, students can design practicums to solve
problems related to the motion of objects on a roller
coaster trajectory.
3.1.3 Analysis of Student Needs
Analysis of student needs for STEM-based practicum
e-modules on the law of conservation of energy is
carried out by distributing questionnaires to students
who have contracted Basic Physics courses. The
questionnaire consists of 3 parts: an analysis of the
use of practicum modules in general, an analysis of
the use of practicum modules on the law of
conservation of energy, and an analysis of the
usefulness and components of the module. The
questionnaire consists of 17 questions, with details of
16 questions being fixed responses and one other
question being an open question. The number of
respondents to the questionnaire is 80 students. Based
on the results of the needs analysis that has been
carried out at the define stage, a practicum e-module
is needed to help guide the practice of the law of
conservation of energy with the following
specifications: (1) The module is solving practical
problems and only contains guiding questions so that
students can solve and design own practicum, (2)
Integrate technological advances (software) to help
analyze the physics data of the practicum results (3)
Have an attractive design and contain various
representations (video, images, text, animation, etc.),
(3) Easy to access using a PC or mobile and does not
require ample storage space.
3.2 Design
At the design stage, the researcher outlines the e-
module that will be developed. The outline of the
STEM-based e-module on energy conservation law
material consists of a Cover, Preface, Table of
Contents, Description of the Practicum Module,
Instructions for the use of the Module, Graduate
Learning Outcomes, Course Learning Outcomes,
Course Learning Sub-Achievements, Learning
Objectives, Real World Problems, Tools and
Materials, Exploration, Conclusions, and
Bibliography. The module outline or writing plan
containing a module's outlines is then developed at
the development stage.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
48

3.3 Develop
The development stage aims to produce a STEM-
based e-module on the material of the law of
conservation of energy that is valid and practical.
However, the research achievements reported in this
progress report have only reached the stage of
validator evaluation. In contrast, trials for students to
see the practicality of e-modules have yet to be
carried out.
The development stage is done by developing the
module outline that was prepared at the design stage.
The outline was developed in Microsoft Word, which
will later be converted to PDF format and flipped
using Flip PDF Corporate software. The cover
display of STEM-based e-modules on the law of
conservation of energy can be seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The cover display of STEM-based e-modules.
The validator then evaluates the product that has been
developed. The validator consists of media experts
and material experts.
3.3.1 Product Validation Results by Media
Expert Validators
Three media expert validators validated the
developed e-module with an instrument in the form
of a questionnaire. The questionnaire for product
assessment in terms of media consists of 3 aspects,
namely appearance, presentation, and quality of
supporting media, which are translated into ten
statements. The results of the media expert validation
are presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Media Expert Validation Results.
No
Assessment
Aspect
Total
Score
Max
Score
Percentage
(%)
1. Appearance 32 36 88.89
2. Presentation 36 36 100
3. Supporting
media quality
46 48 95.83
Final Score Overall Media Expert
Validation (%)
94.91
In Table 2, the percentage of the final value of the
overall media expert validation is 94.91%, with very
high interpretation criteria.
3.3.2 Product Validation Results by Material
Expert Validators
Three material expert validators has validated the
developed e-module with an instrument in the form
of a questionnaire. The questionnaire for product
assessment in terms of the material consists of 3
aspects, namely the suitability of practicum
objectives with learning outcomes, clarity of
practicum series, and STEM components, which are
translated into 11 statements. The results of the
material expert validation are presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Material Expert Validation Results.
N
o Assessment Aspect Total
Scores
Max
Score
Percentage
(%)
1.
Conformity of
practicum objectives
with learning
outcomes
24 24 100
2.
Explanation of the
p
ractical circuit
56 60 93.33
3.
STEM Components
44 48 91.67
Final Score Overall Media Expert
Validation (%)
95.00
In Table 3, the percentage of the final value of the
overall material expert validation is 95.00% with very
high interpretation criteria.
The research product in the form of a STEM-
based practicum e-module has been successfully
developed through this research. The developed
products are categorized as valid for use in learning
activities based on the assessment of media and
material experts. Media experts provide assessments
related to three aspects, namely appearance,
presentation, and quality of supporting media, each of
which meets valid criteria. From the appearance
aspect, the design, colour composition, and
appearance of the letters are appropriate and
attractive. The presentation aspect gets the maximum
percentage, meaning that the e-module is presented
wholly and systematically to facilitate the
achievement of learning objectives. The next aspect
of the media expert's assessment is the quality of the
supporting media. Supporting media here include
pictures and videos so that they are multi-
representative to support students in solving the
Development of STEM Based e-Module Using Flip PDF Corporate on Energy Conservation Law Materials
49

problems presented. In addition to assessments from
media experts, there are also assessments from
material experts covering three aspects: the suitability
of practicum objectives and learning outcomes,
clarity of practicum sequences, and STEM
components, which also receive assessments with
valid criteria.
The aspect of conformity of practicum objectives
with learning outcomes gets the maximum rating
from the validator. This means that the practicum
objectives in the e-module are by the learning
outcomes to be achieved and have been formulated at
the defining stage. The next aspect is the practical
aspect. The practicum series is presented by
considering the complexity of the problems and their
suitability for application at the higher education
level. To support problem-solving, the e-module is
equipped with a video that presents real-world
problems and illustrated images adapted to the
existing concepts in the material on the Law of
Conservation of Energy. The e-module is made so
that students can design their practicum to reach
solutions to the problems to be solved so that the
questions presented at the exploration stage are
constructed correctly and correctly according to the
concepts in the Law of Conservation of Energy
material. The third aspect is the STEM component
aspect. The e-modules developed for practicum
activities have facilitated aspects of science,
technology, engineering, and mathematics in the
STEM approach presented in the practicum series.
This research has only reached the stage of testing
the validity level of the developed media. Follow-up
is needed from this research, namely to determine the
level of practicality of the developed media. A
practicality test is needed to see whether the media
developed meets students' needs and the desired
product specifications based on the results of the
media development needs analysis (Wulandari et al.,
2022). In addition to validity and practicality, this
media also needs to be implemented in learning to see
the effectiveness of the media being developed so that
it can have a good influence on learning. These
influences include increasing problem-solving
abilities, creative thinking abilities and students'
understanding of concepts (Zulaiha & Kusuma,
2020).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research that has been
carried out, it can be concluded that:
1)
The STEM-based practicum e-module on the law
of energy conservation has been successfully
developed through the 4D development method.
The steps taken to produce a research product in
the form of an e-module are defined, designed,
and develop (up to the evaluation stage of the
validator).
2)
The validity of the STEM-based practicum e-
module on the conservation of energy law
material based on media experts gets a
percentage of 94.91% with valid criteria
covering aspects of the display, presentation, and
quality of supporting media. Based on the
material expert, the validity of the e-module gets
a percentage of 95.00% with the criteria of valid,
covering aspects of the suitability of practicum
objectives with learning outcomes, clarity of
practicum series, and STEM components.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank the head of the Basic
Physics Laboratory of the University of Siliwangi for
the support and encouragement of this research. The
fund DIPA Ministry of Research, Technology and
Higher Education, University of Siliwangi, supported
this project.
REFERENCES
Arisya, F., Haryati, S., & Holiwarni, B. (2021).
Pengembangan Modul Berbasis Stem (Science,
Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) Pada
Materi Sifat Koligatif Larutan.
Jurnal Pendidikan
Kimia Universitas Riau
, 6(1), 37–44.
https://doi.org/10.33578/jpk-unri.v6i1.7787
Maulidah, R., Mahmudah, I., & Sulistyaningsih, D. (2022).
The Development of Laboratory-Scaled Mini Roller
Coaster Media for Non-Conservative Energy
Observations
. https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.21-12-
2021.2317271
Prastowo, A. (2012). Panduan Kreatif Membuat Bahan
Ajar Inovatif
. Yogyakarta: DIVA Press.
Pratiwi, W. O. (2021).
Pengembangan Modul Elektronik
IPA Terpada Berbasis Pendekatan STEM untuk
Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berpikir Kreatif Peserta
Didik
. UIN Raden Intan Lampung.
Riduwan. (2010).
Belajar Mudah Penelitian Pemula.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sari, N. (2020). Pengembangan Modul Fisika Berbasis
STEM dengan Strategi Inkuiri Terbimbing pada Materi
Usaha dan Energi Kelas X SMA/MA
. IAIN
Batusangkar.
Sulistyaningsih, D., Maulidah, R., & Mahmudah, I. R.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
50

(2022). Utilization of Video-Based Laboratory ( VBL )
Using Tracker for Analysis of Object Motion on the
Laboratory-Scaled Mini Roller Coaster. ICMScE.
Susanti, A. (2020).
Pengembangan Modul Biologi Berbasis
Stem (Science Technology Engineering and
Mathematich) Pada Peserta Didik MAN 1 Lampung
Barat
[UIN Raden Intan Lampung].
http://repository.radenintan.ac.id/id/eprint/13101
Susanti, E., Maulidah, R., & Makiyah, Y. S. (2021).
Analysis of problem-solving ability of physics
education students in STEM-based project based
learning.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
2104(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-
6596/2104/1/012005
Syahirah, M., Anwar, L., & Holiwarni, B. (2020).
Pengembangan Modul Berbasis STEM (Science,
Technology, Engineering And Mathematics) Pada
Pokok Bahasan Elektrokimia.
Jurnal Pijar Mipa, 15(4),
317–324. https://doi.org/10.29303/jpm.v15i4.1602
Wulandari, S., Surahman, E., & Sulistyaningsih, D. (2022).
Discovery Learning Berbantuan Software Modellus
Pada Pokok
. 8(November), 317–327.
Zulaiha, F., & Kusuma, D. (2020). Pengembangan Modul
Berbasis STEM untuk Siswa SMP.
Jurnal Pendidikan
Fisika dan Teknologi
, 6(2), 246–255.
https://doi.org/10.29303/jpft.v6i2.2182
Development of STEM Based e-Module Using Flip PDF Corporate on Energy Conservation Law Materials
51
