
The Influence of Self-Efficacy and Learning Motivation on Students’
Autonomous Learning in the Digital Era
Armiati
a
, Rose Rahmidani
b
and Dessi Susanti
c
Department of Economic Education, Universitas Negeri Padang, Prof. Hamka Street, Air Tawar, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Self-Efficacy, Learning Motivation, Autonomous Learning.
Abstract: The purpose of the study is to ascertain and analyze 1) The Influence of Self-Efficacy on learning motivation;
2) The Influence of Self-Efficacy on students’ autonomous learning through Learning Motivation. This type
of research is quantitative with an associative type. The sampling technique used in this study was proportional
random sampling with a random number of members from each sub-population with a sample of 217 students.
The data used are primary. The data collection technique is in the form of a questionnaire. Data analysis used
descriptive analysis, analysis prerequisite test, path analysis, t-test, and coefficient of determination. The
analysis tool uses SPSS with an alpha of 0.05. The results showed that 1) Self-Efficacy has a significant
influence on Learning Motivation and 2) Through learning motivation as an intervening variable, self-efficacy
has no impact on students' autonomous learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of the affective aspect is crucial for
enhancing student character. The character can be
interpreted as a vessel of different psychological traits
that help a person adapt to numerous environmental
situations they may face. In addition, A character is
essential to developing and producing a wonderful
human resource, and an independent character is one
of them, especially in facing various challenges in the
digital era (Walker and Graham 2021).
Successful learning can be gained by being more
independence. Independent includes initiating
behavior, overcoming obstacles or problems, having
self-confidence, and being able to do things by
themselves. Independent persons have a desire to do
things by themselves and are capable to find the
solution to their problems. The independence of
students in the digital era should be well developed
because of the ease of access obtained in finding
learning resources and learning new things through
technology (Johnsen and Goree 2021)
In fact, improvement in how Vocational high
school prepares students to be independent character
is required. In teaching and learning activities, the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8457-4834
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2953-6979
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3376-8775
students of Vocational High School 6 Padang have
obtained the theory and practice material that can be
applied during the learning so that students are
expected to be independent.
The initial observations results revealed that the
level of student autonomous learning in the Eleventh
grade at Vocational High School 6 Padang was not
sufficient, out of 30 students only 46.6% of them
actively asked questions in learning. 43.3% lack
initiative to increase knowledge by additional books
from library. The teacher also notes that only a few
students are eager to ask questions throughout the
learning; instead, they are more likely to accept the
information offered by the teacher, whether or not
they fully comprehend it. According to mass media,
some students are absent, less motivated, and lack of
goals for their future (Esra and Sevilen 2021). The
adolescent problems above indicate a lack of
awareness of responsibility and independence in
learning. This phenomenon can cause problems when
they attend higher education (Crome, Farrar, and
O’Connor 2009).
A factor that influences students’ autonomous
learning is self-efficacy. furthermore, other factors
that influence students’ autonomous learning include
200
Armiati, ., Rahmidani, R. and Susanti, D.
The Influence of Self-Efficacy and Learning Motivation on Students’ Autonomous Learning in the Digital Era.
DOI: 10.5220/0012198500003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 200-205
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

self-efficacy, motivation, and goals (Cobb Jr 2003).
The ability or competency of a person to carry out a
task, accomplish a goal, or get through challenges
while learning is known as self-efficacy. Self-efficacy
is the belief in their ability to train their self-control
over the phenomenon in their environment (Bandura,
in (Feist and Feist 2010); (Bandura 2013); (Bandura
2012). Self-efficacy is reflected in the students
themselves through a learning process that occurs
through interaction with the environment.
Based on Schunk's opinion, self-efficacy can
perform during academic learning. Before engaging
in learning activities, Students have different beliefs
about how to gain information, demonstrate skills,
master a subject, and many other things (Schunk
1991). Personal factors together with situational
factors (teacher rewards and feedback), such as goal
setting and information processing can influence
student learning.
Aside from self-efficacy, another factor that
influences students’ autonomous learning is learning
motivation. Students' motivation is positively related
to students’ autonomous learning (Cobb Jr 2003).
Students must be motivated to implement strategies
that will impact the learning process.
Motivation is something that drives a person or
group of people toward doing or not doing something
as an active momentum (Dörnyei, Muir, and Ibrahim
2014). Motives become active at certain times,
especially when the need to achieve a goal is urgent
or felt.
Students’ autonomous learning is closely related
to learning motivation (Schunk and Mullen 2012).
Strong motivation to achieve the goal is necessary for
building intelligence. If a strong motivation has
emerged, it will create an attitude of independence in
the student. Students' self-efficacy affects their
motivation to learn. A person with high self-efficacy
will be more motivated to learn. This is reflected in
someone’s efforts and persistence in overcoming
obstacles. People with high self-efficacy will work
harder to get beyond the obstacles.
Motivation can be an intervening variable to
determine the influence of self-efficacy on students’
autonomous learning. In line with the results of
previous research that has tested the influence of self-
efficacy on students’ autonomous learning with
motivation as the intervening variable. (Anderson,
Hattie, and Hamilton 2005), (Cherian and Jacob
2013) found that students' autonomous learning and
self-efficacy are positively correlated. Subsequent
research by (Kurniyawati 2012) found that self-
efficacy and motivation have a positive and
significant relationship. Good self-efficacy will help
students to achieve good motivation so that students
can complete assignments optimally. The purpose of
this study was to analyze the influence of self-
efficacy on learning motivation and the influence of
self-efficacy on students’ autonomous learning
through learning motivation. (Karnedi, Zaim 2021)
found that students lacked motivation in studying.
Both internal and external factors contributed to this
cause.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
Ex post facto research design is used in this
quantitative research type. The population was 473
students of Eleventh grade at Vocational High School
6 Padang with 217 samples through proportional
random sampling technique. The exogenous variable
in this study is self-efficacy, the endogenous variable
is students’ autonomous learning and the intervening
variable is learning motivation.
A questionnaire is used to collect the data. Before
collecting the data, instrument validation were done
to obtain valid and reliable instruments. The results of
the variable testing on students’ autonomous learning
are 18 valid statements with very high reliability from
Cronbach's Alpha value of 0.901. In the Self-Efficacy
variable, there are 14 valid statements with very high
reliability, with a Cronbach Alpha value of 0.880.
Furthermore, on the learning motivation variable,
there are 23 valid statements with very high reliability
from the Cronbach Alpha value of 0.887.
Before analyzing the data, analysis prerequisite tests
were obtained, such as the normality test and
heteroscedasticity test. To see the influence between
variables by using path analysis (Path Analysis) with
the SPSS application. The path model in this study can
be described as follows:
Figure 1: Research path model.
Furthermore, the t-test is used to see whether the
proposed hypothesis is proven or not, with the
criterion that if the significant value is <0.05 then Ho
is rejected and Ha is accepted.
Self-efficacy
(X)
Learning
motivation
(
Z
)
Autonomous
learning (Y)
ρzx
ρyz
ρyx
The Influence of Self-Efficacy and Learning Motivation on Students’ Autonomous Learning in the Digital Era
201
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Result
Respondents in this study were 217 students of
Eleventh grade at Vocational High School 6 Padang
The number of female respondents was 191 students,
more dominant than male students, only 26 students.
Based on the respondent’s answers, the results of the
frequency distribution of the research variables are
shown in the following table:
Table 1: Distribution of Independent Learning scores.
Indicator Mean TCR (%) Description
Learnin
g
activit
y
4,08 81,65 Good
Persistence of
learnin
g
activities
3,54 71,09 Quite good
Learnin
g
direction 3,64 72,88 Quite
g
oo
d
Learning
creativit
y
3,83 76,69 Quite good
Avera
g
e 3,77 75,57 Quite
g
ood
Table 2: Distribution of Learning Motivation scores.
Indicator Mean TCR(%) Descri
p
tion
Desire to succee
d
3,98 79,81 Good
Motivation and needs
for learning
4,36 87,39 Good
Future goal and
p
urpose
4,28
85,78 Good
Learning rewards
4,16 83,46 Goo
d
Interesting activities
4,06 80,24 Goo
d
Conducive learning
environment
3,89 77,92 Quite good
Average 4,12 82,43 Good
Table 3: Distribution of Self-Efficacy Scores.
Indikator Mean TCR(%) Keteran
g
an
L
evel 4,00 80.11 Good
Stren
g
ht 4,03 80,80 Goo
d
Generalit
y
4,04 80,91 Goo
d
Rata-rata 4,02 80,60 Good
Table 4: Normality Test.
One-Sam
p
le Kolmo
g
orov-Smirnov Test
Unstanda
r
d
ized Resi
d
ual
N 217
No
r
mal
Parameters
a,b
Mean ,0000000
Std.
Deviation
5,54425041
Most Ext
r
eme
Differences
A
b
solute ,041
Positive ,041
Ne
g
ative -,041
K
olmo
g
o
r
ov-S
m
i
r
nov Z ,604
As
y
m
p
. Si
g
.
(
2-tailed
)
,858
a. Test
d
ist
r
ibution is No
r
mal.
b
. Calculate
d
f
r
om data.
Table 5: Heteroscedasticity Test.
Coefficien
t
s
a
Model
Unstanda
r
d
ize
d
Coefficients
Standardize
d
Coefficients
T Sig.
B Std. Er
r
o
r
Beta
1
(
Constant
)
1,913 2,383 ,803 ,423
Self Efficac
y
(
X
)
-,045 ,055 -,077 -,807 ,420
Motivation
(
Z
)
,052 ,032 ,155 1,618 ,107
a. Dependent Variable: Abs_Res
Table 6: Coefficient of Self-Efficacy on Learning
Motivation.
Coefficients
a
Model
U
nstandardize
d
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig.
B Std.
Erro
r
Beta
(Constant)
26,494 4,701 5,636 ,000
ED 1,210 ,083 ,706 14,612 ,000
a. Dependent Variable: KM
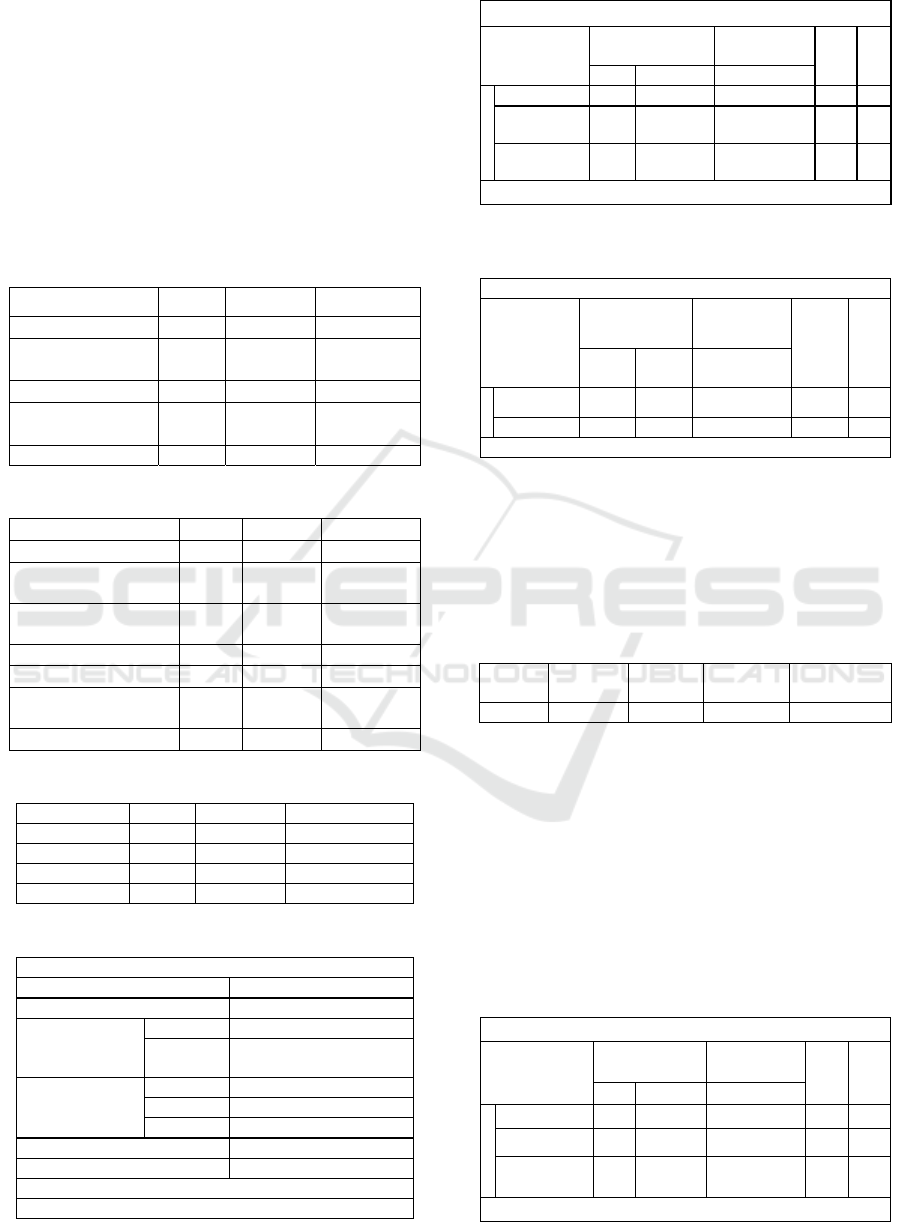
The coefficient of self-efficacy (X) on learning
motivation (Z) is 0.706, the t count is 14.612 and the
significance is 0.000 <0.05. This demonstrates how
learning motivation (Z) was impacted by self-
efficacy
(X).
Table 7: Coefficient of Determination, Sub Structure 1.
Model Summar
y
Model R R Square
Adjusted
R S
q
uare
Std. Error of
the Estimate
1 ,706
a
,498 ,496 7,24451
a. Predictors: (Constant), ED
Self-efficacy variable (X) has a 0.498 coefficient of
influence on learning motivation (Z). This means that
the self-efficacy variable contributes to learning
motivation by 49.8%. While the remaining 50.2% is
influenced by other variables. Mathematically, the
empirical model of the influence of self-efficacy (X)
on learning motivation (Z) is stated as follows: Y =
Pzx + ε
1
, Y = 0.706x + 0.502ɛ
1
.
Table 8: Coefficient of Self-Efficacy and Learning
Motivation on Students’ Autonomous Learning.
Coefficients
a
Model
U
nstandardize
d
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig.
B Std. Erro
r
Beta
1
(Constant)
9,315 3,872 2,406 ,017
Efikasi Diri
,474 ,090 ,354 5,278 ,000
Motivasi
Belaja
r
,330 ,052 ,423 6,302 ,000
a. Dependent Variable: kemandirian belajar
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
202

The coefficient of self-efficacy (X) on students’
autonomous learning is shown by the value of
Standardized Coefficients beta is 0.354. The t count
is 5.278 and the significance is 0.000 <0.05. This
means that there is an influence of self-efficacy (X)
on students’ autonomous learning (Y).
The coefficient of learning motivation (Z) on
students’ autonomous learning (Y) is indicated by the
value of Standardized Coefficients beta is 0.423. The
t count is 6.302 and the significance is 0.000 <0.05.
This shows that there is an influence of learning
motivation on students’ autonomous learning.
Table 9: Coefficient of Determination, Sub Structure 2.
Model Summar
y
Model R R Square
Adjusted R
Square
Std. Error of
the Estimate
1 ,718
a
,516 ,512 5,57010
a. Predictors: (Constant), motivasi belajar, efikasi diri
b. Dependent Variable : Kemandirian Belajar
The influence of self-efficacy variables (X) and
learning motivation (Z) is 0.516. This means that the
variables of self-efficacy and learning motivation
contribute to students’ autonomous learning by
51.6%. While the remaining 48.8% is affected by
other variables. Mathematically, the empirical model
of the influence of self-efficacy (X) and learning
motivation (Z) on students’ autonomous learning (Y)
is stated as follows: Y = Pyx + Pyz + ε2, Y = 0.354x
+ 0.423z + 0.484ɛ2
From the results of the data analysis above
,
the
following path structure is created by considering the
impact of exogenous and endogenous variables on the
dependent variable:
Figure 2: Complete path model of test results.
Table 10: Direct and Indirect Influence of the Path
Coefficient of each variable.
No
Variable
influence
Influence
Total
Direct Indirect
1 X towar
d
Y 0,354 0,032 0,386
2 X towar
d
Z 0,706 - 0,706
3 Z towar
d
Y 0,423 - 0,423
Based on the table above, therefore it can be said
that the contribution of self-efficacy (X) to
autonomous learning (Y) is 0.354 or 35.4%,
meanwhile, the indirect contribution of self-efficacy
and learning motivation to autonomous learning is
0.032 or 3.2 %. The direct contribution of learning
motivation (Z) to students’ autonomous learning (Y)
is 0.423 or 42.3%. So it showed that the contribution
of the direct influence is bigger than the indirect
influence. This means that learning motivation as an
intervening variable does not play a role in increasing
student students’ autonomous learning to increase
students’ autonomous learning is enough by
increasing self-efficacy in students.
3.2 Discussion
3.2.1 The Influence of Self-Efficacy on
Student Learning Motivation
According to the analysis of the first hypothesis test's
findings, self-efficacy has an impact on student's
motivation to learn. The student is more motivated to
learn when they have a better sense of self-efficacy.
Self-efficacy is an individual believes that he
feels capable of overcoming many things including
the actions needed to achieve goals. Meanwhile,
motivation is an encouragement that comes from
inside and outside a person who is trying to find the
desire to succeed in forming experiences and
exercises that influence his behavior. Students who
have strong self-efficacy and believe in their
abilities, these students will be motivated to achieve
their goals in learning, such as a sense of willingness
to get appreciation from the teacher and to achieve
goals in the future (Schunk & Miller, 2002).
Self-efficacy is a factor in learning motivation; a
person with a high level of self-efficacy will be more
motivated. (Pervin & Jhon, in Bandura, 2013). The
more self-efficacy a person has, the more motivated
they are to study. This is reflected in the effort and
persistence in overcoming existing obstacles. When
he faced difficulties, he will continue to perform his
duties and not give up easily. People with high self-
efficacy will use more effort to get beyond
challenges.
High self-efficacy makes students more confident
in having efforts to achieve good learning outcomes,
Students can easily handle situations and manage
demands that arise from both within themselves and
the environment because they have control over their
emotions and their ability to act (Zimmerman, B.J,
2000). Strong self-efficacy can increase learning
motivation in achieving learning achievement at
Pzx=0,706
Pyz=0,423
Self-efficacy
(X)
Learning
motivation (Z)
Autonomous
learning (Y)
ɛ
1
=0,502
ɛ
2
=0,484
Pyx=0,35
The Influence of Self-Efficacy and Learning Motivation on Students’ Autonomous Learning in the Digital Era
203

school, and students' strong belief can solve
problems or difficulties that will be faced. To enable
the students to confidently resolve the problem they
encounter at school (Pervin & Jhon in Bandura,
2013).
The findings of this study are consistent with the
research conducted by Kurniawati (2012) and Budi,
Santosa, and Suhendro (2018) who found that Self-
efficacy and learning motivation are positively and
significantly correlated. This demonstrates that
having high levels of self-efficacy will also assist
students to develop good learning motivation and
enable them to finish assignments successfully.
3.2.2 The Influence of Self-Efficacy on
Students’ Autonomous Learning
Through Learning Motivation as an
Intervening Variable
Based on the results of the analysis test in the second
hypothesis, it revealed that the value of Z count <Z
table, which means that the parameter is not
significant. The direct influence of self-efficacy on
autonomous learning is bigger than the indirect
influence of self-efficacy on autonomous learning
through motivation.
Students with high levels of self-efficacy will be
highly motivated to learn in their learning. Students
will believe in themselves to do difficult tasks and try
to deal with obstacles. In other words, students who
have low self-efficacy typically lack confidence in
their abilities. The ability of a student's self-efficacy
plays a very important role in increasing learning
motivation because belief in one's abilities will
motivate students to be actively involved in ongoing
learning.
Based on Kurniawati's research (2012) shows that
Self-efficacy and learning motivation are positively
and significantly correlated. However, The findings
of this study show that learning motivation in
Eleventh-grade students at Vocational High School 6
Padang is unable of being mediation to strengthen
students’ autonomous learning. Learning motivation
plays no role in increasing students’ autonomous
learning to increase students’ autonomous learning it
is sufficient for students by increasing their self-
efficacy.
According to Cobb (2003), the factors that
influence students’ autonomous learning include self-
efficacy, motivation, and goals. Bandura in Jess Feist
& Gregory J. Feist (2012) argues that when someone
has high self-efficacy, they will have a strong
capacity to control their actions. Accordingly, the
degree of self-regulation in terms of independence
increases as self-efficacy increases. Students' self-
efficacy has an important role in increasing
autonomous learning because the foundation of self-
efficacy is having belief in someone’s ability to
engage actively and autonomously in learning
activities.
The results of this study are supported by the
results of research conducted previously by Devi
(2016) it shows that self-efficacy is the belief that one
can act in a way that will result in the desired behavior
in a certain circumstance. Consequently, having
strong self-efficacy will improve a person's
performance in general. Furthermore, research by
Adicondro and Purnamasari (2011), February (2016),
and Sari et al., (2017) shows that there is a positive
relationship between self-efficacy and students’
autonomous learning. Self-efficacy is a measurement
of a student's confidence in his or her ability to carry
out a task, accomplish a goal, or get beyond a learning
obstacle.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results study, it represents that: (1) Self-
efficacy has a direct influence on student students’
autonomous learning. This implies that students' self-
efficacy will rise along with their level of autonomous
learning. (2) Self-efficacy has no influence on student
students’ autonomous learning through learning
motivation as an intervening variable. As a result,
motivation cannot be considered an intervening
variable between students' self-efficacy and
independent learning. To promote students'
autonomous learning, self-efficacy must be
increased.
Considering the result of this study, the
suggestions provided are: (1) Students can increase
their self-efficacy by believing that they can complete
a task and achieve positive learning results. Along
with enjoying the challenge of difficult tasks and
working in groups rather than doing it alone to
exchange opinions. (2) Students have a desire to learn
on their own so that they can become more
autonomous and responsible. Additionally, students
look for sources of information about a subject more
frequently to expand their knowledge rather than just
studying for tests, and (3) To develop an active desire
to learn and become skilled students, they can
increase their learning motivation. It is believed that
this would prevent students from easily giving up
when they encounter learning difficulties.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
204

REFERENCES
Anderson, Angelika, John Hattie, and Richard J. Hamilton.
2005. “Locus of Control, Self‐Efficacy, and Motivation
in Different Schools: Is Moderation the Key to
Success?” Educational Psychology 25(5):517–35.
Bandura, Albert. 2012. “On the Functional Properties of
Perceived Self-Efficacy Revisited.” Journal of
Management 38(1):9–44.
Bandura, Albert. 2013. “The Role of Self-Efficacy in Goal-
Based Motivation.”
Cherian, Jacob, and Jolly Jacob. 2013. “Impact of Self
Efficacy on Motivation and Performance of
Employees.”
Cobb Jr, Robert. 2003. “The Relationship between Self-
Regulated Learning Behaviors and Academic
Performance in Web-Based Courses.”
Crome, Keith, Ruth Farrar, and Patrick O’Connor. 2009.
“What Is Autonomous Learning?” Discourse: Learning
and Teaching in Philosophical and Religious Studies
9(1):111–25.
Dörnyei, Zoltán, Christine Muir, and Zana Ibrahim. 2014.
“Directed Motivational Currents.” Motivation and
Foreign Language Learning: From Theory to Practice
9–30.
Esra, MEŞE, and Çiğdem Sevilen. 2021. “Factors
Influencing EFL Students’ Motivation in Online
Learning: A Qualitative Case Study.” Journal of
Educational Technology and Online Learning 4(1):11–
22.
Feist, Jess, and Gregory J. Feist. 2010. “Teori
Kepribadian.” Jakarta: Salemba Humanika 31.
Johnsen, Susan K., and Krystal K. Goree. 2021. “Teaching
Gifted Students through Independent Study.” Pp. 445–
78 in Methods and materials for teaching the gifted.
Routledge.
Karnedi, Zaim, Mukhaiyar. 2021. “Seven C’s
Communication Skills Problems in Writing Business
Letter of English Major Undergraduate Students.”
Kurniyawati, Rita. 2012. “Hubungan Antara Efikasi Diri
Dengan Motivasi Belajar Siswa.”
Schunk, Dale H. 1991. “Self-Efficacy and Academic
Motivation.” Educational Psychologist 26(3–4):207–31.
Schunk, Dale H., and Carol A. Mullen. 2012. “Self-
Efficacy as an Engaged Learner.” Handbook of
Research on Student Engagement 219–35.
Walker, Sue, and Linda Graham. 2021. “At Risk Students
and Teacher-Student Relationships: Student
Characteristics, Attitudes to School and Classroom
Climate.” International Journal of Inclusive Education
25(8):896–913.
The Influence of Self-Efficacy and Learning Motivation on Students’ Autonomous Learning in the Digital Era
205
