
Analysis of the Implementation of the Independent Curriculum
Program at the Middle School Level Through Mathematics Teaching
Modules
Nola Nari, Christina Khaidir, Nurhizrah Gustituati and Alwen Bentri
University Doctoral Degree Students, Padang State University & Padang State University, Indonesia
gustituatinurhizrah@gmail.com, alwenbentri@fip.unp.ac.id
Keywords: Independent Curriculum, Teaching Module.
Abstract: Implementation of independent curriculum problems occur at each component structure and education unit.
These circumstances become the focus of the problems that are necessary to find the solution. One of them is
the implementation of an independent curriculum through the teacher as means of strengthening the profile
of Pancasila students. This study aims to analyze the concept, the advantages of an independent curriculum,
and the implementation of the independent curriculum through the teaching module as the meaning of
strengthening the profile of Pancasila students. This study uses a qualitative approach. The informants of this
study are chosen by using a purposive sampling technique. The data collection process is carried out with
deep interviews, documentation studies, and field notes. The data analysis is carried out by referring to the
Miles and Huberman model. To ensure the validity of the researcher's data, the researcher uses the
triangulation technique and upgrades the researcher’s persistence in analyzing the document found. The
results of the research show that the concept and the advantages of an independent curriculum are that the
material is simpler and deeper, more independent for students, educators, and education units, and more
relevant and interactive in strengthening the profile of Pancasila students. The implementation of the teacher’s
teaching module in learning is to pay more attention to individual diversity so that the students’ talents and
interests are noticed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Independent curriculum according to the National
Education Standards Board is a learning curriculum
that refers to the talents and interests’ approach.
Independent curriculum was issued by Indonesian
government through long episodes rolled out by the
Ministry of Education. In the first episode, the
independent curriculum discusses about the
replacement of National exams, the termination of
national-ranged school exams (USBN), the
simplification of lesson plan and the acceptance of
new student based on zoning. In the 5th episode, the
government issued and riving teacher (Nailyl
Maghfiroh, 2022);((Kemdikbud, 2022).
Many models and variations were implemented by
each school that was begun with survey electronically
done by the education authorities where the options
of the implementation of the independent curriculum
are independent sharing, self-changing, and
independent learning. Those third choices submitted
to school previously through opinion polls or survey
needs related with what to be the potentials as well as
the readiness of every school in implementing the
curriculum. At the highest level, the implementation
of the independent curriculum is in the third option,
which is the independent sharing. Every school that
chooses independent sharing program will apply
independent curriculum by developing the teaching
device where this activity started a driving teacher in
the school. Independent changing in independent
curriculum means that where teacher in the school
will develop or take existing teaching device
developed and adapted with the school’s needs.
Meanwhile, the simplest choice for independent
curriculum that is with the choice of independent
sharing where some parts from independent
curriculum principle can be applied permanently by
using 2013 curriculum without replacing it
completely. The various applications done by every
school with the same educational level naturally will
280
Nari, N., Khaidir, C., Gustituati, N. and Bentri, A.
Analysis of the Implementation of the Independent Curriculum Program at the Middle School Level Through Mathematics Teaching Modules.
DOI: 10.5220/0012199700003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 280-286
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

raises difference later to the learning results that will
be obtained by each student with the same
educational level(Fajri, 2019).
In the implementation of independent curriculum,
the central government delivers fully the
implementation of management and assistance to the
local government by pointing as well as facilitating
with people who already designated at the center to
become the main companion toward changes, which
involved driving teacher. Driving teacher are teachers
who have follow training for 9 months with activities
arranged systematically so that later there will be
capable teachers that can be a motivator as well as a
catalyst to the change that want to be achieved in
independent Curriculum. Survey shows that in West
Sumatra, the numbers of driving teachers are not
many. Every school of course applies the
implementation of independent curriculum but on the
option of independent sharing only a number of new
schools that have a driving teacher so that the school
can operate independent sharing as well. This finding
raises the gap in between educator, student, and
school. Based on that, it will impact to the student’s
study results later nationally (Safrizal, 2022).
The implementation of independent curriculum
carried out in West Sumatra will give good impact if
it is applied well. This thing can occur if every teacher
follows training implementation and apply in learning
pretty well. The problem aside also happens in
schools that do not have a driving teacher. The spread
and the equity of driving teacher training must
become government’s attention so that all teachers
and schools are capable to implement independent
curriculum pretty well, so students will obtain the
appropriate education results with the expected
independent curriculum. Based on that thing, the aim
of this writing is for analyzing the implementation of
independent curriculum through teacher’s teaching
module for strengthening the profile of Pancasila
students.
2 METHOD
The method used in this study is qualitative approach
with the type of the research is in the form of content
analysis. This study is conducted by building and
describing the concept studied naturally and facts
found in the field, so that credible and accessible data
can be accounted scientifically. The informants
chosen in this study were chosen by using purposive
sampling with criteria in accordance with data
requirements. The technique used to choose the
informants is the informants that are capable to serve
description related to the implementation of the
independent curriculum through driving teachers and
non-driving teachers for strengthening the profile of
Pancasila students. The data collection was carried
out based on interview that related to what the driving
teacher and non-driving teacher as well as how every
teacher develops module in accordance with the
students' talent desired in the independent curriculum.
Besides deep interview, the document that related to
the implementation of independent curriculum was
further analyzed and done by referring to the miles
and Huberman model so that it can ensure the data
validation is carried out within deep understanding
and accuracy related to the program document of the
implementation of independent curriculum through
driving teachers proclaimed by the Ministry of
Education and Culture(Creswell, 2013); (Miles,
1994); (Sugiyono, 2018).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The research findings obtained from various sources
and information obtained from the informants, and it
will be explained the analysis of the results related to
the implementation program of independent
curriculum, that is the concept and the advantages of
independent curriculum, the implementation of
independent curriculum through teacher’s teaching
module in learning.
3.1 Independent Curriculum Concepts
and Advantages
The draft about the implementation of independent
curriculum as the data analyzing results has been
collected through key information nor key content
scattered in various sources and obtained from
internet through numbers of concepts about the
implementation of independent curriculum.
According to the definition of independent
curriculum based on National Education Standards
Board, independent curriculum is a learning
curriculum that the implementation refers to students’
talents and interests’ approach. Independent
curriculum is the continuation of the direction of
previous curriculum development such as 2006
curriculum, 2013 curriculum, emergency curriculum,
prototype curriculum, and other previous
curriculums. The red thread of this curriculum
development are: the first were the holistic orientation
where the curriculum designed for developing
holistically take in intelligence and academic skill,
non-academic spiritual, and social emotional
Analysis of the Implementation of the Independent Curriculum Program at the Middle School Level Through Mathematics Teaching
Modules
281
cognitive competence. The second one are the bases
on development of the independent curriculum but
the competence is not the content to refer the designed
curriculum based on desired competence that want to
be developed and not based on content or certain
theories. The third is that the independent curriculum
is more contextually and personalization in which the
curriculum designed in accordance with the local
culture context, the school’s vision and mission, the
local environment and the students’ needs.
There are three superiorities of independent
curriculum: the first is that the independent
curriculum is simple and deeper where the focus is on
the essential material and the competence
development of the student at each phase and
expected to be deeper, meaningful, no rush and fun.
The second superiority of the independent curriculum
is more independent. Independent here means that
students can choose the subject in accordance with
their interests and talents. Meanwhile, the teachers
can teach in accordance with the achievement and
development level of the students whatever the
teachers designed. In learning, the teachers are
independent by considering important how the
students in learning can study well. Furthermore, the
education unit can also be independent that means the
education unit has authority for developing and
managing curriculum as well as learning in
accordance with characteristics of the education unit
and the students. The third superiority of the
independent curriculum is relevant and interactive
where the independent curriculum gives opportunity
for school to develop its superior program that will be
conducted through project activities where through
this project activities give more opportunities to
students for exploring actively about the actual issues
for example environment issues, health issues, culture
issues and others where each issue is developed
through the project can develop the character and the
competence of the profile of Pancasila students.
Figure 1: Basic Framework for the Independent
Curriculum.
Viewed from the framework of the independent
curriculum in figure 1 is known to be the national
goals level and profile of Pancasila students were set
by the government centrally. Meanwhile, the content
standards, process standards and evaluation standards
and other standards uniformly also determined by the
government centrally. Then each education unit can
design how the curriculum structure can be achieved
in accordance with the learning achievements
formulated in school’s vision, mission principles
learning as well as the assessment. The learning
achievements are developed by each teacher with
refers to vision and mission of the education unit. The
context and local policy is also the main thing that
must be noticed in developing the learning
achievements.
The structure of the independent curriculum has
peculiarity from curriculums that existed before. On
the independent curriculum, the most prominent
characteristics to surface especially at the junior high
school level which is in the independent curriculum
is conducted by the adjustment to the development of
digital technology. Informatics subjects becomes the
subject required where previously in the 2013
curriculum informatics subject was deleted and
merged to other subjects with no time allocation
specially for the informatics subject. Then, in the
independent curriculum, there is project-based
learning for strengthening the profile of Pancasila
students that is conducted at least three times in a year
or three times every school year.
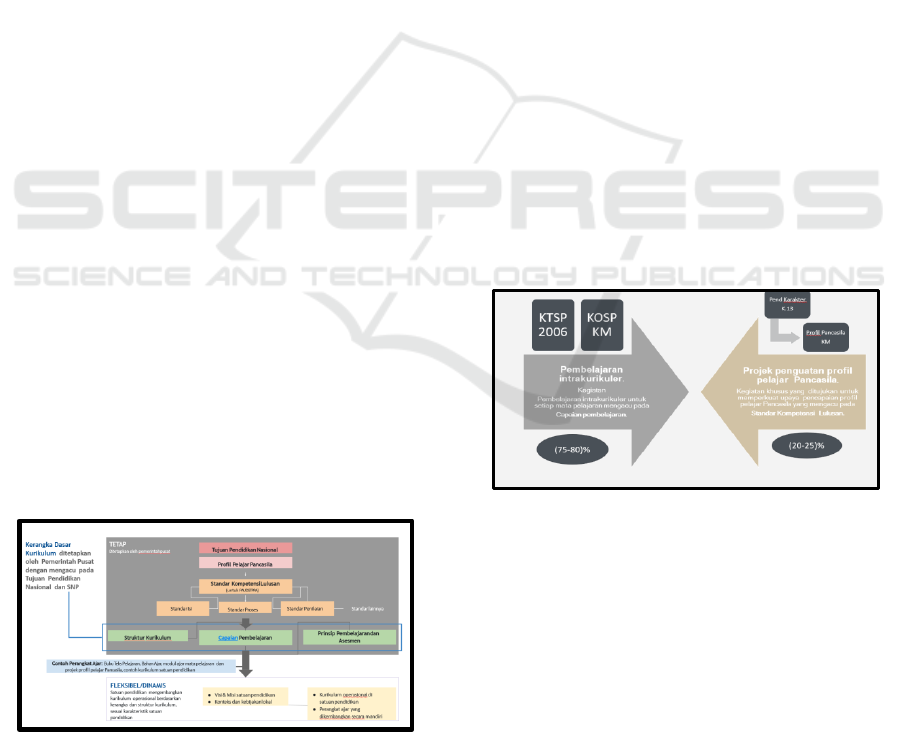
Figure 2: Analysis Results of Structure of Independent
Curriculum.
The curriculum structure in the independent
curriculum were at least having two big components
to be main part of the independent curriculum. Based
on Figure 1. it is known that in independent
curriculum there are intracurricular learningand
projects to strengthen the profile of Pancasila
students. On the first point, there is intracurricular
learning where every subject refers to learning
achievements with the learning time weight is 75% to
80% of time or the total time provided for every
learning subject. The material of the subjects of the
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
282

title of the learning at the junior high school level are
not too many namely religion, Pancasila, Indonesian
literature, Mathematics, Science, Social Studies,
Physical education sports and health, Informatics, Art
and English. In independent curriculum,
intracurricular learning is arranged in operational
curriculum of the education unit. The operational
curriculum of education unit in the independent
curriculum has similarity with the previous existing
curriculum which is the level of the curriculum from
education units that was issued and used in 2006 for
the operating curriculum of education unit in
independent curriculum developed by
operationalizing the vision, the mission of education
unit and the local culture context. On the education
unit level curriculum that existed in 2006, the
teaching tools were developed by each teacher in
accordance with the education unit
characteristics(Ansyar, 2015). Now the independent
curriculum is also designed by each teacher in
accordance with the talents and interests of each
student in strengthening the profile of Pancasila
students(Sayyidi, 2020).
The second component in the independent
curriculum structure is the strengthening project of
the profile of Pancasila students, it is a particular
activity designated specifically for strengthening the
effort to achieve the profile in learning Pancasila that
the results finally later will refers to the competence
standard of the graduates. In the independent
curriculum there is local content that become the
typical characteristic of the curriculum where the
education unit can add the local content set by the
local government in accordance with the local
characteristics. The education unit can add the
additional content in accordance with the
characteristics of the education unit history flexible
through three choices; first, the education unit can
integrate to the subject. For example, in learning
mathematics, we integrate the local content with the
local cultures for example with traditional house,
local craft named songket or Minangkabau carvings
that is known with mathematics term that refers to
ethno math. These conduct the integration to the
theme of strengthening project for the Pancasila
profile as an example for the program like
"Baliak ka Surau". The third, the education unit can
develop subject which stands alone, for example in
Bukittinggi there is Minangkabau natural culture
learning that becomes the school subject.
In the independent curriculum, we know with
term learning achievements. Learning achievements
is a target that must be filled by the students when
learning intracurricular subject. Learning
achievement is learning competence that must be
achieved by the student at every phase started from
foundation on Early Childhood Education for basic
and intermediate education. The learning
achievements arranged for every learning. This thing
refers to decision of Minister of Indonesia number
56/M/2022 concerning the curriculum application
guidelines in order to recovery learning. The
government only set the final goals and the phase time
whereas the education unit have discretion to
determine the strategies and methods or plot for
reaching it in order to determine the required
appropriate strategy.
There are 5 components of the learning
achievements; the first is the subject rational, the
second is the goals of lesson, and the third is the
subject characteristics, the fourth is the subject
achievements in every phase overall, and the fifth is
the achievement of every phase according to the
element.
Education unit operational Curriculum developed
to show suitability with the characteristics and the
needs of the students in the local and education unit.
In the development and the management of operating
curriculum, The Education Unit includes whole
stakeholders’ interest that consist of students,
committee school and community. Principle
development operations curriculum in the Education
Unit with at least the first 5 points must be centered
to participating in education that is learning the must
Fulfill diversity potency needs development and
stages study as well as interest participant educate.
The profile of Pancasila students always becomes
referred to each step in drafting operational school
curriculum. Both must be contextual which means
that it shows peculiarity and characteristics unit of the
social context and work and industrial environment
that shows characteristics from study participants in
the area. Third principle is developing curriculum to
load essential information or the main thing that is
needed and used for Education unit. Language must
be used straightforward to concise acknowledgement.
which leads us to the fourth principle that develop
independent curriculum that is accountable and mean
that it could be held accountable by data-based and
actual occurrence. While the fifth involves various
stakeholders’ interests.
3.2 Implementation of Independent
Curriculum Through Teacher
Teaching Modules in Learning
Teaching tools are various materials used by
educators or inner teacher effort reach profile
Pancasila students and achievements learning.
Teaching modules include book text lessons, teaching
modules, reinforcement projects profile Pancasila
Analysis of the Implementation of the Independent Curriculum Program at the Middle School Level Through Mathematics Teaching
Modules
283

students, examples curriculum operational Education
units, learning videos as well as forms other.
According to Nana Sujana, module is a completed
tool measurement where the learning module have
roles and tasks in the independent manner because it
could use for units and all other units .(Wijaya,
1988).Leaning module could interpreted as study
planned through the planned activity at a time
arranged in a systematic manner. Whereas teaching
modules in the curriculum independent is number of
Tools or facilities, media, methods, instructions and
guidelines designed in a manner systematic and
interesting. The teaching module is implementation
from plot destination developed learning from
achievements learning with profile learn Pancasila as
the target.
The teaching module is a document that contains
objectives, steps and learning media as well as the
required assessment in one unit or topics based on
plot destination learning. Destination development
teaching module is to help educator in doing learning.
Educators have independence for choose or modify
teaching materials that already provided by the
government through the independent platform.
There are some eligible criterion owned by the
existing teaching modules :1. Essential, it means
understanding draft from every eye lesson through
study experience and cross discipline, 2. Interesting,
meaningful and challenging where the results of the
teaching modules must grow interest for learn and
engage education participants with the active manner
on learning process, 3. Relevant and contextual, it
means to develop teaching modules that related with
knowledge and experience possessed before with the
time context and place at the fourth serial that must
owned by learning for continuity which means plot
activity in accordance with study participant
education.
Figure 3: Components of the Independent Curriculum
Teaching Module.
Kindly, general teaching module has three
components: 1. Information, 2. Components and 3.
Attachments. General information contains writer’s
identity from the module, profile of Pancasila
students, targets and infrastructure, target for
education participants and learning models used for
reaching destination of the expected learning process.
The core component of study consists of destination
learning, assessment, experience meaning, question
lighter, activity reflection participant study and
reflected educator. Component from attachment
teaching module includes from sheet work material,
enrichment educators, students, glossary and
bibliography. Broadly speaking, third component
arranged in a manner systematic and owned by
students and developed by the participants
themselves to educate participants characteristics that
they taught.
Teaching modules are arranged in accordance with
phase or the steps of students’ development that
considers what is learned with destination learning
and based development period long. Independent
educator can adapt teaching module from students’
characteristics or by arranging an appropriate
standalone teaching module with students’
characteristics. existing LKPD in teaching module
can created educator so that they will be capable to
accommodate various student needs.
Figure 4: LKPD according to student needs.
Based on figure 4 above we can conclude that in
developed teaching modules, the driving teachers
were arranged by 3 kinds of LKPD used in learning.
LKPD type 1 is given to students with ability that
contains main question in the LKPD. LKPD type 2 is
given to current capable students so that it will help
with the task hook while LKPD type 3 is given to
student with low capability. For students in this case,
LKPD is compiled in a manner systematic so that the
main tasks is described more detail and to become
more sub item complex so that students with low
capability can complete tasks on LKPD with a decent
amount of level with students that has a good
capability(Nari, 2017); (Putri Indah Sari, 2021).
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
284

4 DISCUSSION
Findings on the study result shows that
implementation of independent curriculum to be
something mandatory that conducted for resolving
various weaknesses in the curriculum previously so
that every student fulfilled rights and freedom in
education, however directed with well by the teacher
with appropriate utilization of the teaching module by
students’ characteristics. Various components and
structures available in independent curriculum were
capable to develop students competency through
intracurricular learning and reinforcement profile of
Pancasila students through the possibility of
integrated activity project with eye lesson or stand up
alone so that generated strong student in a manner
academic and own character in accordance aspects
expected by the profile Pancasila (Sayyidi,
2020)students ; (Ihsan, 2022).
In the previous text, it already outlined that
independent curriculum draft already gave
superiority because it is more simple and deep by the
amount of the theory learning that seems more simple
because physics, biology, history and geography on
curriculum were previously merged into science
learning in the independent curriculum, however
payload theory had taught deeper and contextual so
that it will capable to generate a project for strengthen
profile of Pancasila students from students. In
implementation of the independent curriculum,
students must choose one certain major but given the
freedom in accordance to their talents and interests.
So is the teacher, in terms of their chose material to
their teaching methods and process, each teacher is
given freedom to design it alone the teaching module
in accordance characteristics material and
characteristics participant the students he teaches
with especially formerly identify participant educate
through question designed lighter at the beginning
learning. Question lighter could form diagnostic test
so with results test the teacher is able group student in
accordance ability, method learning, talent as well as
each other's interests. From the results the diagnostic
test the teacher can design appropriate LKPD needs
participant educate(Hattarina, 2022); (Putri Indah
Sari, 2021); (Hadi, 2015).
In learning mathematics there is some steps you
can conduct to students in solving problem, for one
according with the polya description to understand
problem, make plans, implement plan and check
return correctness answer (Fariha Mpar August,
2021); (Netriwati, 2016); (Astutiania, 2019). For
students with decent capability, LKPD is designed for
direct main tasks with an example like what is the
volume of the block with its known elements. For
students with low capability will be given additional
question for more simple acknowledgment on student
with the help of solving problem steps according to
polya. Based on student characteristics difference just
now, more independent teachers that designs
worksheets on appropriate teaching modules for
students. The next superiority in the independent
curriculum are the developed materials and projects
that are more relevant with students nor learning
environment, and more interactive. From the clear
exposure that independent curriculum
implementation has is something that is mandatory
held with priority main which were the students and
driving teachers.
If implementation of the independent curriculum
could be implemented pretty good, it might become a
decent change towards students nor educator.
Students could learned pretty well through capable
driving teachers as they becomes good locomotor for
capable move towards the student for study through
designed teaching modules in accordance with needs
and in the end will formed understanding meaning for
students, shaping characters, strengthening the profile
of Pancasila students and will give a good end
cognitive results for students(Kahfi, 2022).
The limited research by understanding related
implementation of independent curriculum in middle
school; through teacher means as a solution for
develop and prepare students quality and
reinforcement of the profile of Pancasila students in
face progress of time, so correlated with the resulting
driving government through special training for
capable and appropriate learning designs with
Indonesia's education target and strengthening the
profile of Pancasila student. The research weakness
to this is that it’s pretty much limited to execution
conducted interviews through perceived online
suboptimal, however with studies of the document
that is done, it becomes a gap for held more study.
Study about implementation of the independent
curriculum through reinforcement programs for the
profile of Pancasila students and its influence were to
be formatting the character profile on Pancasila
students which leads to the topics of study interest for
described in the research so that it could enrich
outlook knowledge and depth knowledge related with
implementation of independence curriculum to begin
with held in the beginning year of its implementation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The implementation of Independent Curriculum as
proclaimed by the Minister of Education and Culture
Analysis of the Implementation of the Independent Curriculum Program at the Middle School Level Through Mathematics Teaching
Modules
285

becomes means of improvement and development
sustainable education unit especially the students and
educators. This can be seen from the concept and the
advantages of independent curriculum, the
implementation of independent curriculum through
teacher’s teaching module as well implementation in
learning.
Related to the implementation of the independent
curriculum, the sustainable monitoring and coaching
by the central and local government can be done in
accordance concept that has been developed so that
there is education equity, achievement of the goals of
national education and reinforcement of the profile of
Pancasila student.
REFERENCES
Ansyar, M. (2015). Kurikulum: Hakikat, Fondasi, Desain
dan Pengembangan. Jakarta: Kencana.
Astutiania, R. (2019). .Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah
Matematika dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Cerita
Berdasarkan Langkah Polya. Prosiding Seminar
NasionalPascasarjana UNNES, 297-303.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Qualitatuve Inquiry & Research
Design (3rd ed.). London: Sage Publication.
Fajri, K. N. (2019). Proses Pengembangan. Islamika, 35-48.
Fariha Mpar August, d. (2021). Analisis Kemampuan
Pemecahan Masalah Matematis Siswa berdasar
prosedur Polya. Jurnal ilmiah Pendidikan Matematika
Vol 6, No 1 (2021), 43.
Hadi, S. (2015). Pengembangan Sistem Tes Diagnostik
Kesulitan Belajar . Jurnal Penelitian dan Evaluasi
Pendidikan Volume 19, No 2, Desember 2015 (168-
175), 168-175.
Hattarina, S. (2022). Implementasi Kurikulum Medeka
Belajar Di Lembaga Pendidikan. Seminar Nasional
Sosial Sains, Pendidikan, Humaniora (SENASSDRA)
Volume 1, 181 – 192, 2022, 182.
Ihsan, M. (2022). Kesiapan Guru Terhadap Implementasi
Kurikulum Merdeka Belajar. Seri Publikasi
Pembelajaran Vol. 1 No. 1 (2022): Isu-Isu
Kontemporer-AKBK3701, 37-46.
Kahfi, A. (2022). Implementasi profil pelajar Pancasila dan
Implikasinya terhadap karakter siswa di sekolah.
Dirasah: Jurnal pemikiran dan Pendidikan Dasar, 138-
151.
Kemdikbud. (2022, Desember 3).
https://sekolah.penggerak.kemdikbud.go.id/. Retrieved
from https://sekolah.penggerak.kemdikbud.go.id/:
https://sekolah.penggerak.kemdikbud.go.id/
Miles, M. B. (1994). Qualitative Data Analysis (2nd ed).
London: Sage Publication Inc.
Nailyl Maghfiroh, d. (2022). Implementasi Kurikulum
Merdeka Belajar Kampus Merdeka Dalam Menghadapi
Era Disrupsi Dan Era Society 5.0. Jurnal Inspirasi
Manajemen Pendidikan Volume 09 Nomor 05 Tahun
2022, 1185-1196, 1185.
Nari, N. (2017). Analisis Kemampuan Pemecahan masalah
Mahasiswa calon pendidik Matematika. Ta'dib, 137-
147.
Netriwati, N. (2016). Analisis Kemampuan Mahasiswa
dalam Pemecahkan Masalah Matematis menurut Teori
Polya. Al-Jabar : Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika , 20.
Putri Indah Sari, N. N. (2021). Pengembangan LKPD
Geometri Bangun Datar Berbasis Arsitektur Rumah
Gadang Minangkabau. CIRCLE: Jurnal Pendidikan
Matematika 1 (02), 28-38, 28-38.
Safrizal, S. (2022). Analysis of Guru Penggerak Programs
as Sustainable Professional Development for Teachers.
Al-Ishlah: Jurnal Pendidikan,Vol. 4, 1 (April 2022):
2135-2142, 2135-2142.
Sayyidi, S. &. (2020). Reaktualisasi Pendidikan Karakter di
Era. Bidayatuna: Jurnal Pendidikan Guru Mandrasah
Ibtidaiyah
, 502.
Sugiyono. (2018). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: Alabeta.
Wijaya, c. d. (1988). Upaya Pembaharuan Pendidikan dan
Pengajaran. Jakarta: Remadja Karya.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
286
